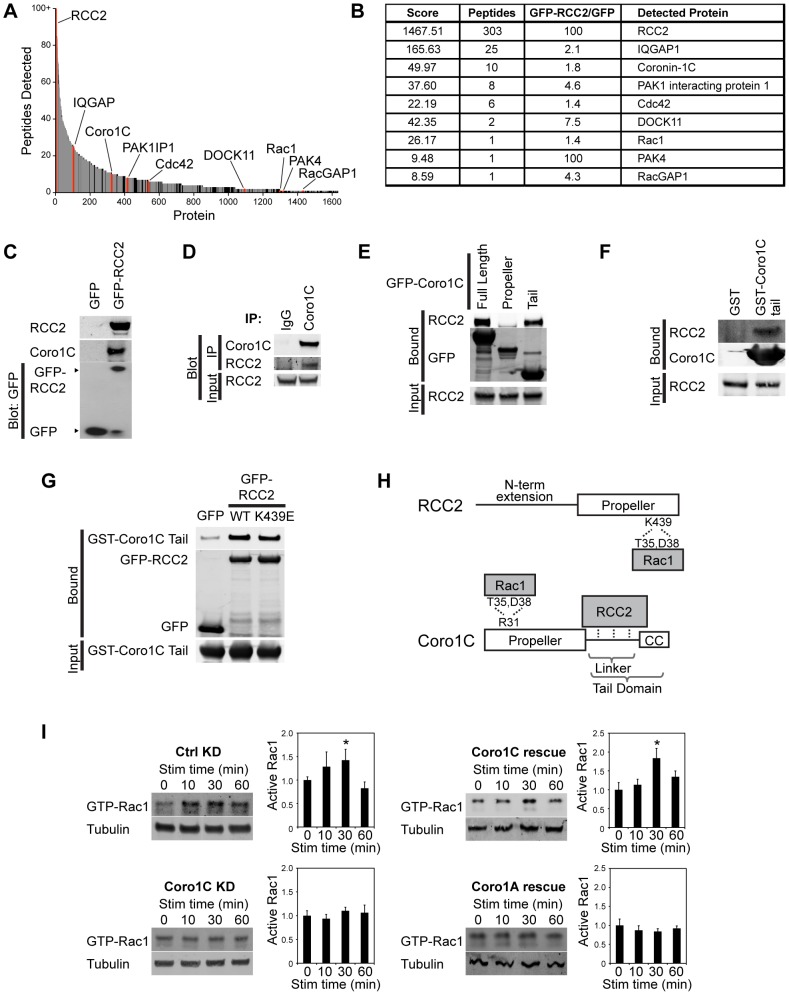
Fig. 3.
The RCC2-binding protein Coro1C is necessary for syndecan-4-stimulated Rac1 activation. (A) Plot of the 1636 proteins identified by SILAC mass spectrometry that associate with GFP–RCC2 better than GFP. Proteins linked to GTPase signaling are in red, nuclear and ribosomal proteins in gray, and other proteins in black. (B) A table of the proteins linked to GTPase signalling, listing score, number of peptide hits and enrichment over GFP alone. (C) Coro1C co-immunoprecipitated (IP) with GFP–RCC2 but not GFP from 293T cells in a GFP-Trap experiment, n = 6. (D) Endogenous RCC2 and Coro1C co-immunoprecipitated from fibroblasts, n = 7. (E) RCC2 co-precipitated from 293T lysates with GFP-Coro1C full length and tail domain, but not propeller domain. n = 5. (F) In vitro translated RCC2 bound to GST-Coro1C tail in a pulldown assay, n = 5. (G) GFP, GFP–RCC2 or GFP–RCC2-K439E beads were incubated with GST–Coro1C tail and blotted for bound tail protein. WT, wild-type. (H) Schematic of the domain structures of RCC2 and Coro1C. (I) H/0-stimulated (Stim) Rac1 activation in control (Ctrl) knockdown (KD) (n = 6), Coro1C-knockdown (n = 8), Coro1C rescue (n = 4) and Coro1C-knockdown and Coro1A rescue (n = 6), and RCC2 and Coro1C double-knockdown MEFs (n = 5). *P<0.05 (ANOVA). Results are mean±s.e.m. Coro1C-knockdown with an alternative oligonucleotide is shown in supplementary material Fig. S1K.