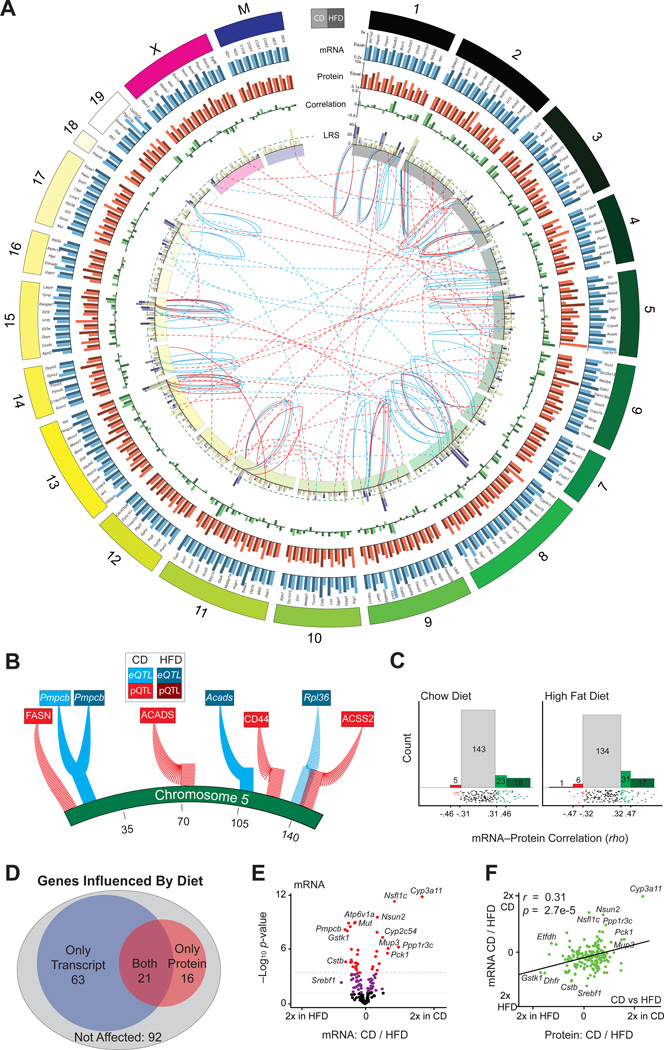
Figure 2. mRNA and Protein Overview.
(A) Circos plot of mRNA and protein data for all 192 genes, labeled on outer edge. Genes are represented by two bars: light for CD and dark for HFD. Genes are arranged by relative chromosome position; the chromosome length is according to number of genes measured. Blue bars indicate the transcript relative expression CD versus HFD; orange bars indicate the protein relative expression CD versus HFD. Bars with more unequal heights indicate diet has a larger impact. Green bars indicate the correlation between the transcript and protein for each gene within each diet. Fuchsia bars represent the strength of the peak eQTL. Yellow bars represent the strength of the peak pQTL. The two bars are overlaid with transparency. The dashed green line represents the simplified significance cutoff (LRS ≥ 18). The inner ring indicates the chromosome location. The blue central lines represent significant eQTLs, and the red central lines represent significant pQTLs. The central solid lines represent cis-QTLs, and the central dashed lines represent trans-QTLs. QTL lines stem from the LRS bar graph and terminate on the inner side of the chromosome ring at the approximate QTL location.
(B) Magnified view of eQTLs and pQTLs mapping to chromosome 5.
(C) In CD ~25% (left), and in HFD ~30% (right), of transcripts correlate nominally significantly with their protein. The lower strip charts show correlation distribution. Spearman correlation values corresponding to nominal significance (p < 0.05) and corrected significance (p < 0.0002) are displayed on the axis.
(D) Venn diagram of genes that are differentially regulated between CD and HFD as transcripts (blue), proteins (red), both (purple), or neither (gray).
(E) Volcano plot for mRNA showing the magnitude of dietary effect versus significance. ~45% vary with nominal significance (p < 0.05) between the dietary conditions. Approximately 19% vary with corrected significance (raw p < 0.0003). Some extreme genes are labeled.
(F) Plot of the effect of diet on transcripts versus the effect of diet on proteins. In general, transcripts and proteins are similarly affected by diet.