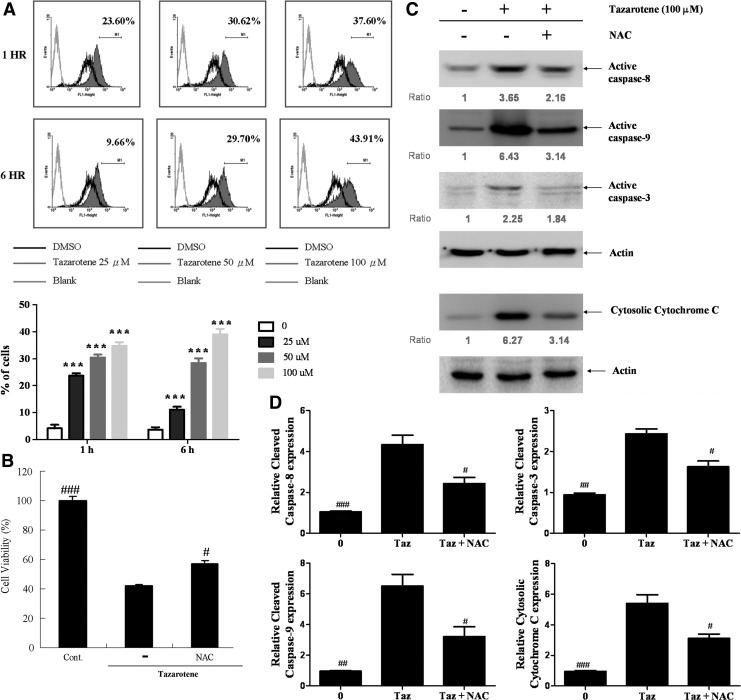
FIG. 5.
The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in tazarotene-induced apoptosis and the reverse effect of oxidant scavengers. (A) BCC cells were exposed to various doses of tazarotene for 1 or 6 h, and ROS levels were analyzed by flow cytometry. The means±SD of the experimental triplicates are presented in the bar graph at the bottom. ***p<0.001, compared with the 0.1% DMSO-treated group. (B) Reversal of 100 μM tazarotene-induced reduction in cell viability. The data represent the means±SD from three wells. The data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. (C) Caspase activation and cytosolic cytochrome c expression induced by the oxidant scavenger N-acetylcysteine in BCC cells. (D) The bands were analyzed by ImageJ and normalized to actin. The means±SD of three independent experiments are presented in the bar graph. #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, and ###p<0.001, compared with the 100 μM tazarotene-treated group.