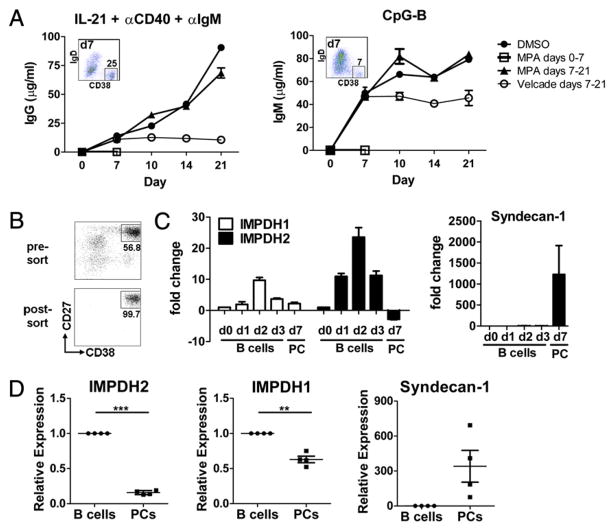
FIGURE 8.
Terminally differentiated PCs have reduced expression of IMPDH2 and are not susceptible to inhibition by MPA. A, Purified B cells were cultured and stimulated as indicated. DMSO control alone, MPA (1.0 μM), or bortezomib (Velcade, 100 ng/ml) was either added at initiation of culture (day 0) or after 7 d of culture. Supernatants were harvested on days 7, 10, 14, and 21, and Ig content was determined by ELISA. Inset indicates the percentage of CD19loIgD−CD38hi PCs in culture on day 7 at the time when DMSO, MPA, or bortezomib was added late. Mean (±SD) of one of three representative experiments is shown. B and C, Purified B cells were stimulated with IL-21, anti-CD40, and anti-IgM and cultured for the days (d) indicated. mRNA was isolated either from unfractionated B cell cultures on days 0, 1, 2, and 3 or from sorted PCs (CD27hiCD38hi) on day 7. B, Pre-sort and post-sort PC fractions on day 7 are shown. C, IMPDH1, IMPDH2, and syndecan-1 levels were quantified by RT-PCR. Fold change shown is relative to resting B cells (day 0). Data represent the mean ± SEM of three donors tested. D, Total B cells and PCs were sort purified from human bone marrow, and expression of IMPDH2, IMPDH1, and syndecan-1 was quantified by RT-PCR. Four unique donors are shown. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005.