Fig. 1.
Introduction of the 2D agent‐based model
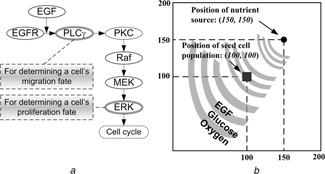
a Schematic representation of the signalling pathway
In short, EGFR is activated by binding to extracellular EGF, inducing receptor dimerisation and autophosphorylation
The bound receptor forms a docking site for the signalling molecule PLCγ, which then activates the Raf signal through PKC
This process initiates the ERK signalling cascade, which is involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. The rates of change of PLCγ and ERK are employed to determine cell migration and proliferation chances for the next step
b Virtual 2D microenvironment with a discrete lattice containing 200 × 200 grid points
A single, distant blood vessel representing a ‘nutrient source’ is located at (150, 150)
The nutrient source is the most attractive location for the chemotactically‐acting tumour cells (i.e. cells tend to move towards the nutrient source)
When the first cell reaches the nutrient source, a simulation run is terminated
The diameter of each cell and the unit interval of the 2D microenvironment are all 10 µm
