Fig. 4. Topical p38MAPK inhibition attenuates acute dermal proinflammatory cytokine expression.
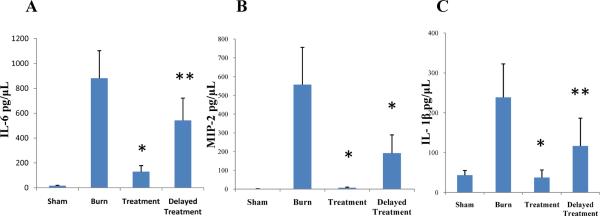
Skin samples, harvested at 12 or 24 hours post-injury, were homogenized and supernatants were processed by ELISA for IL-6 (A), MIP-2 (B) and IL-1β (C) detection. Topical treatment with a p38MAPK inhibitor resulted in significant inhibition of dermal proinflammatory cytokine expression versus untreated burn control with both immediate and delayed (4h post-injury) application. Data presented as mean ± 95% confidence interval. *p < 0.001, **p< 0.03, ANOVA, n= 15 per group (5 animals/group × 3 experiments).
