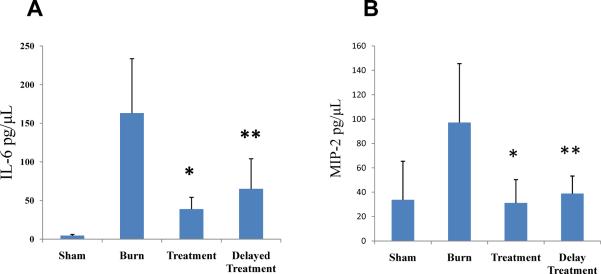
Fig. 6. Topical p38 MAPK inhibition reduces serum IL-6 and MIP-2 levels.
Serum samples were obtained at 24 h post-injury from Sham, untreated burn (Burn), treatment (immediate post-injury) or delayed treatment (4 h post-injury). Serum IL-6 and MIP-2 levels were significantly increased in Burn as compared to sham. Topical p38 MAPK inhibition in burn wounds significantly reduced serum IL-6 and MIP-2 levels in all the treatment groups. Data are represented as mean ± 95% confidence interval. For figure 6(A) * denotes p< 0.001 and ** p<0.05 vs. Burn; for figure 6(B) * denotes p< 0.002 and ** p<0.02 vs. Burn, ANOVA, n= 15 per group (5 animals/group × 3 experiments).