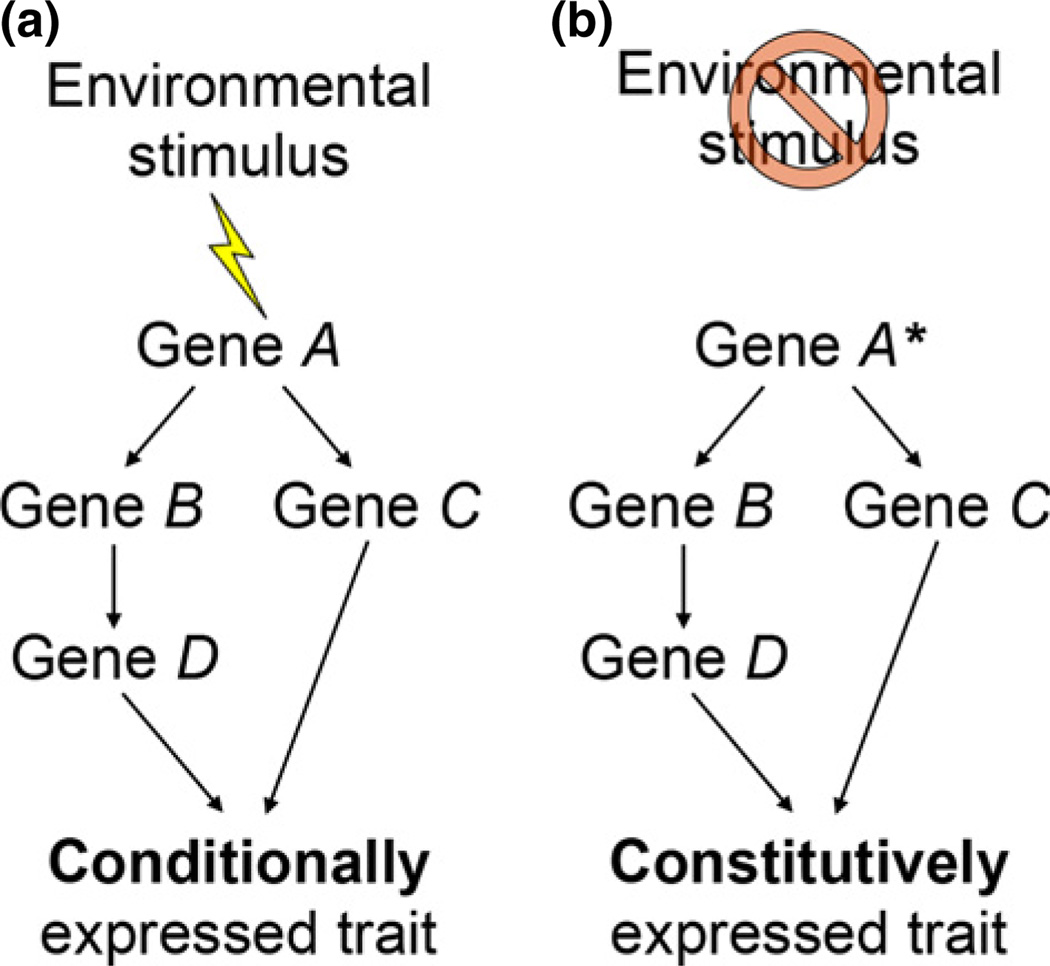
Fig. 2.
Complex, environmentally induced traits are likely specified by gene regulatory networks (GRNs). Moreover, genetic assimilation – when selection causes a trait that was originally environmentally induced to become expressed constitutively – is likely to occur as a result of mutations in upstream elements of these GRNs For example, (a) in an ancestral lineage, an environmental stimulus might be necessary to activate a GRN and produce a particular trait. (b) In a derived lineage, however, a mutation in the upstream element, ‘Gene A’ (indicated here by an asterisk), might result in this trait being produced constitutively, that is, without the original environmental stimulus.