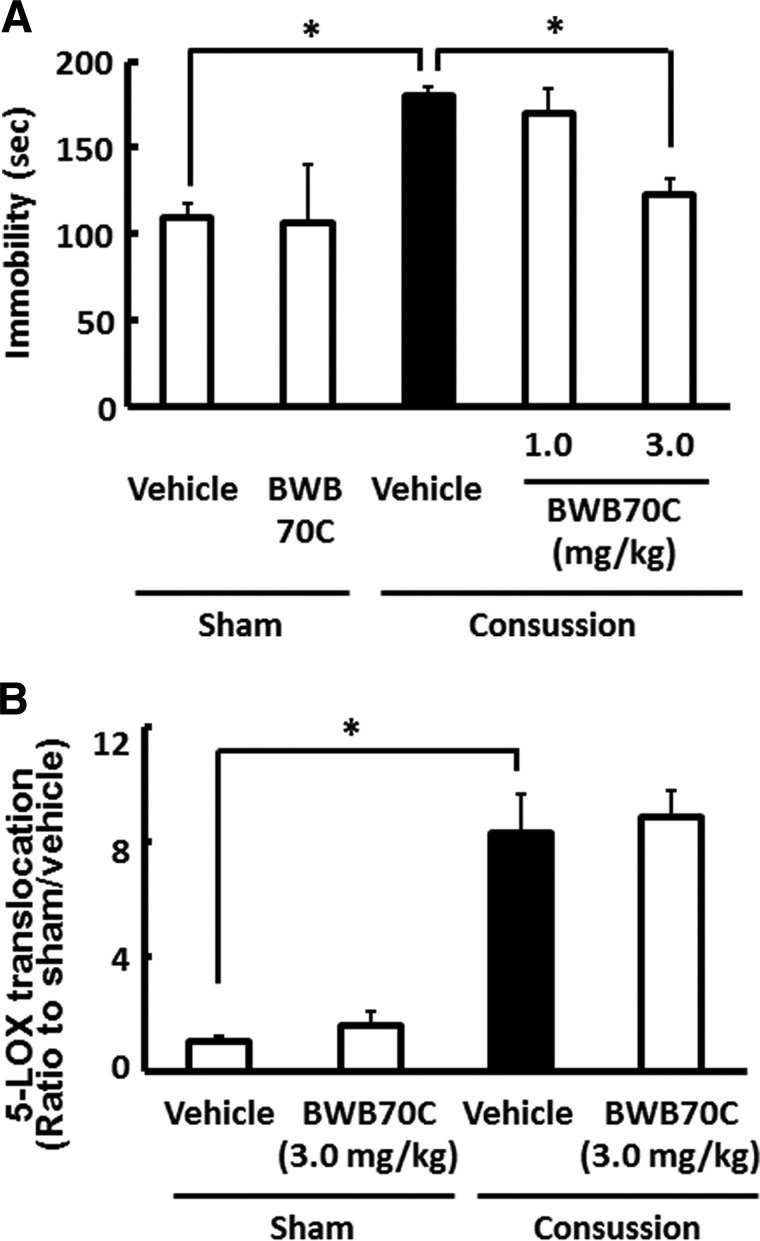
FIG. 6.
Effect of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitor on depressive-like behavior and 5-LOX translocation after concussion. Mice were injected with either the 5-LOX inhibitor, BWB70C (1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg), or vehicle immediately and 1 day after concussion. (A) The forced swim test was performed 3 days postconcussion, and treatment with BWB70C prevented the higher immobility time in vehicle-treated concussed mice. Data are expressed as the mean±standard error of the mean (SEM; sham plus vehicle-treated group, n=4; sham plus BWB70C, n=3; concussion plus vehicle-treated group, n=6; concussion plus BWB70C-treated group, n=5). *p<0.01, compared to the vehicle-treated concussed mice group (black bar). (B) Quantification of 5-LOX translocation to the nuclear envelope 3 h after the last injection of BWB70C (3.0 mg/kg) or vehicle. Mice treated with BWB70C and vehicle showed no significant difference in the increased 5-LOX translocation in the hippocampal astrocytes 24 h after concussion. Data are expressed as the mean±SEM (sham plus vehicle-treated group, n=4; sham plus BWB70C group, n=5; concussion plus vehicle-treated group, n=5; concussion plus BWB70C-treated group, n=5). *p<0.01, compared to the vehicle-treated concussed mice group (black bar).