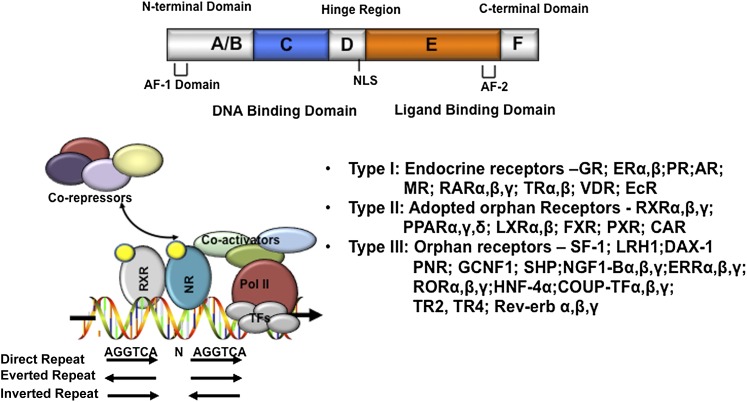
Fig. 6.
Nuclear receptors. The domain structure of nuclear receptors is shown on the top. The putative nuclear receptor response element binding sequences, arranged in direct repeat, everted repeat, and inverted repeat, are shown. Ligand-activated receptors recruit coactivators to replace corepressors, which results in transactivation of target gene expression. Nuclear receptors are classified into three types: type I endocrine receptors, type II adapted orphan receptors, and type III orphan receptors. Refer to Chawla et al. (2001) for details on the nuclear receptor superfamily and nomenclature. AF-1, activation function-1. AF-2, activation function-2; NLS, nuclear localization sequence.