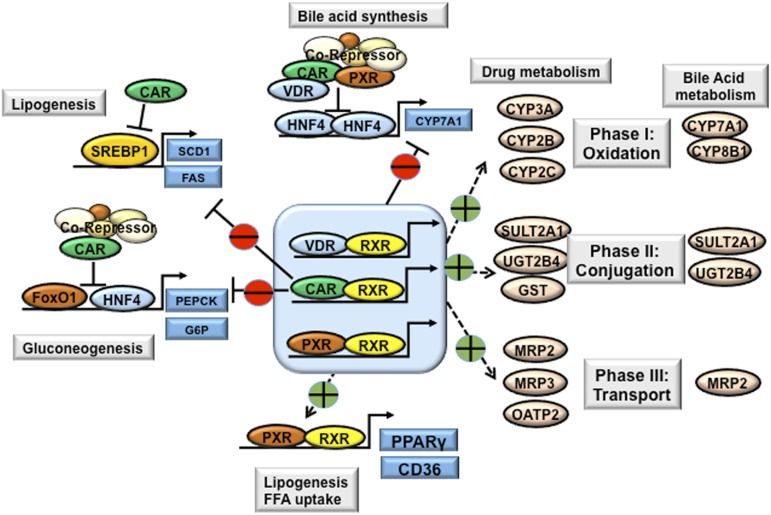
Fig. 7.
Xenobiotic nuclear receptors in bile acid, drug, lipid, and glucose metabolism. The xenobiotic nuclear receptors PXR and CAR are highly expressed in the liver and intestine. VDR is highly expressed in the intestine, but is expressed at low levels in the liver. Activation of xenobiotic nuclear receptors by drugs, bile acids, and xenobiotics induces a network of genes involved in phase I, phase II, and phase III drug and bile acid metabolism and detoxification. CAR, PXR, and VDR inhibit CYP7A1 and thus bile acid synthesis via interaction with HNF4α and inhibition of HNF4α transactivation of CYP7A1. Similarly, CAR inhibits PEPCK and G6Pase involved in gluconeogenesis and inhibits SREBP-1c in lipogenesis. Activation of CAR decreases plasma glucose levels and improves hepatic steatosis in obesity and diabetes. By contrast, activation of PXR induces hepatic expression of PPARγ and CD36, leading to hepatic steatosis. FFA, free fatty acid; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1.