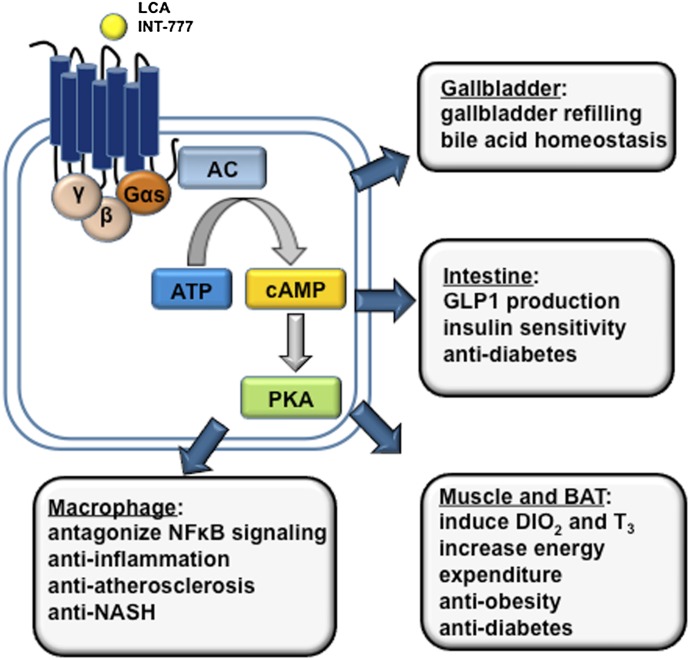
Fig. 8.
Bile acid–activated TGR5 signaling in metabolism and inflammation. TGR5 is activated by secondary LCA and synthetic agonists (e.g., INT-777). TGR5 is a Gαs GPCR that induces cAMP/PKA signaling. TGR5 is expressed in brown adipocytes, macrophages/monocytes and hepatic Kupffer cells, gallbladder epithelium, and intestine, with high levels found in the colon. TGR5 is not expressed in hepatocytes. In brown adipose tissue, TGR5 activation stimulates energy expenditure; in the intestine, TGR5 activation stimulates GLP-1 production from L cells. These metabolic effects underlie the antiobesity and antidiabetic properties of TGR5 agonists. TGR5 activation shows anti-inflammatory effects, and TGR5 activation may protect against colitis, Crohn’s disease, and atherosclerosis. TGR5 in the gallbladder epithelium regulates gallbladder refilling. AC, adenylate cyclase; DIO2, type 2 deiodinase; PKA, protein kinase A; T3, 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine.