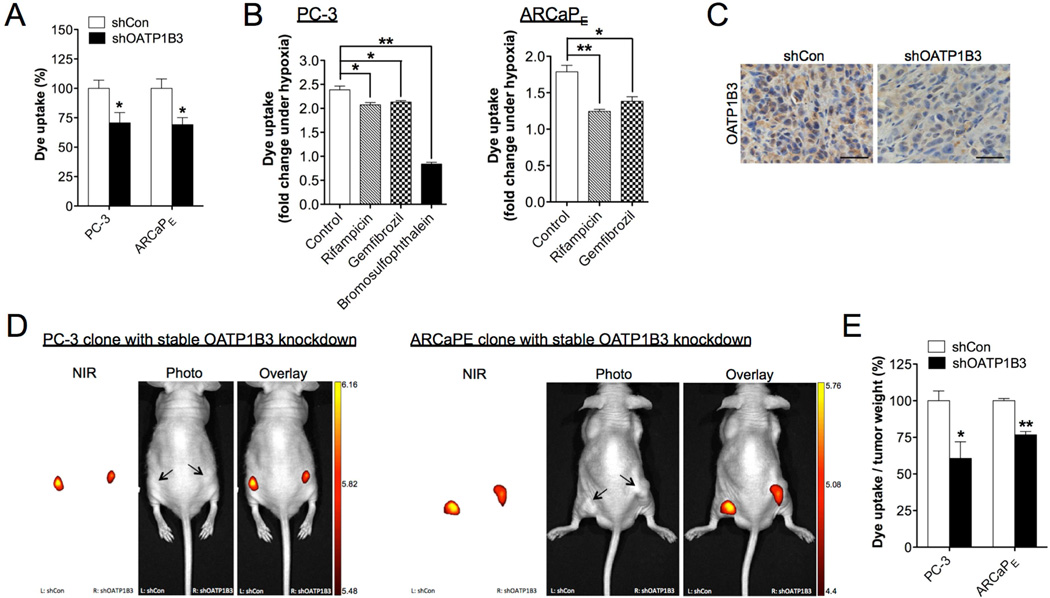
Fig. 5.
OATP1B3 mediated the uptake of MHI-148 dye by cancer cells and tumor xenografts. (A) Determination of MHI-148 dye uptake in PC-3 and ARCaPE cells with stable knockdown of OATP1B3 (N=3, mean ± SEM). (B) Determination of MHI-148 dye uptake in PC-3 (left panel) and ARCaPE (right panel) cells pre-treated with different OATP1B3 selective inhibitors as indicated for 1 hr followed by hypoxia treatment (1% O2, 4 hr). Data was presented as fold change of MHI-148 dye uptake with hypoxia (N=3, mean ± SEM). (C) IHC analysis of OATP1B3 expression in control and OATP1B3-knockdown PC-3 tumor xenograft. Original magnification, x400; scale bars represent 20 µm. (D) Representative in vivo NIRF images of control (left flank)/OATP1B3-knockdown (right flank) PC-3 (left panel) and ARCaPE (right panel) tumor xenografts. Scale bars represent x109 for in vivo NIRF imaging of both PC-3 and ARCaPE tumor xenografts in the unit of radiant efficiency. (E) Quantitation of MHI-148 dye uptake in tumor xenografts (N=5, mean ± SEM), presented as the ratio of dye intensity to tumor weight. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.