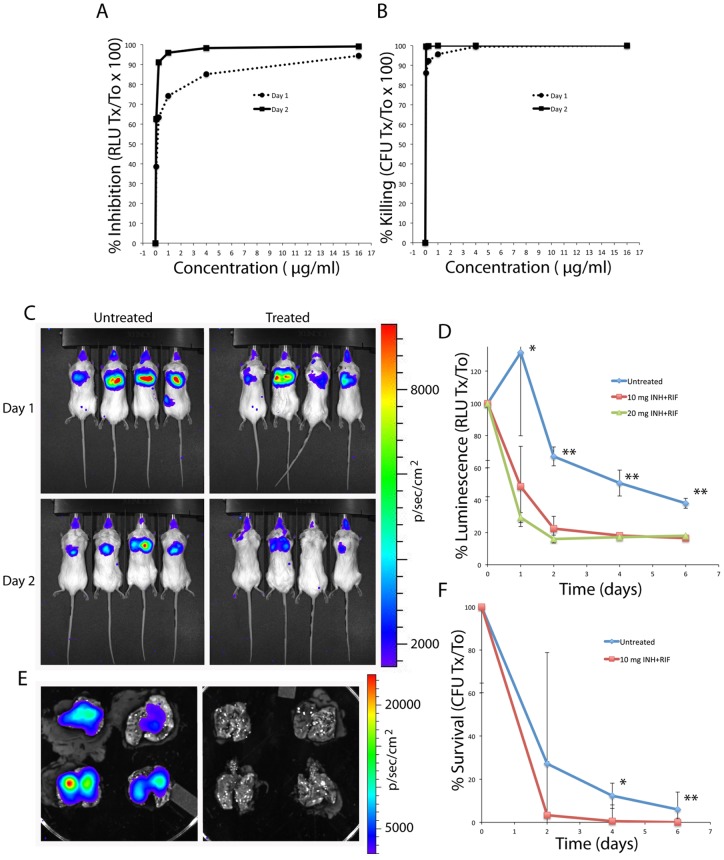
Figure 8. Codon optimized click beetle red luciferase (CBRlux) allows rapid therapeutic evaluation.
Percent inhibition of light production (A) and bacterial killing (B) for 104 of BCG expressing codon optimized CBRlux (optCBRlux) in the presence of different concentrations of isoniazid (INH) plus rifampin (RIF) during culture in bacterial media after 24 (day 1) or 48 h (day 2) as compared to the absence of antimicrobials. Whole body imaging during pulmonary infection in BALB/C mice (4/group) with 4×106 cfu of BCG expressing optCBRlux after 24 and 48 hr treatment with 10 mg/kg INH+RIF results in a reduction in luminescence (C). Quantitation of the percentage of the initial luminescence as compared to each time point out to six days post-treatment confirms the reduced luminescence in treated animals (D). Similarly, ex-vivo imaging of lungs at 2 days to confirm luminescence observed in whole body images is derived from the lungs and is reduced after antibiotic treatment (E). Untreated and treated panels for lung images are indicated in panel C. Correlation of luminescence with cfu present was confirmed by plating homogenates from the same animals at each time point (F). Data and error bars represent the means and standard deviations, respectively, of four mice. * indicates p<0.05 and ** indicates p<0.01 as compared to treated group at the same time point.