Fig. 2.
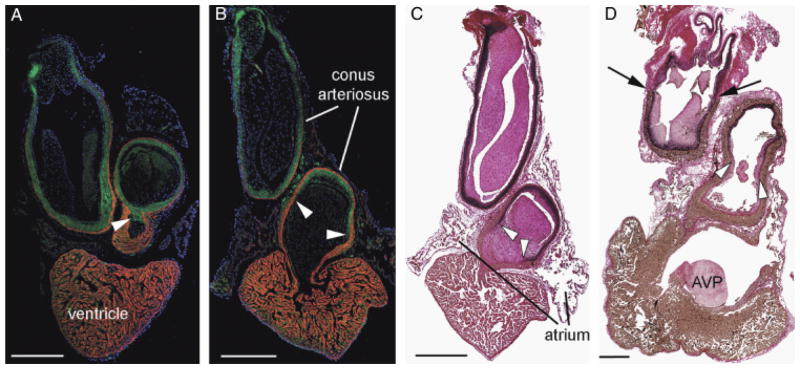
Confirmation of a smooth muscle-myocardium overlap in lungfish species. African (slender) lungfish Protopterus dolloi (A) and South American lungish Lepidosiren paradoxa (B) labeled with CH1 (myocardium—red) and SM22α (green). Cell nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). In each image, cranial is to the top. The smooth muscle of the outflow tract (OFT) extends to the base of the endocardial valves (arrowheads). The myocardial collar extends almost as far as the pericardial wall. Note however that a small portion of the distal OFT contains no myocardium. (C and D) Elastic trichrome stain of Lepidosiren paradoxa (B) and the Australian lungfish Neoceratodus forsteri. Note that similar to in the zebrafish, elastic and fibrous proteins (stained black) coincide with the smooth muscle cells almost to the proximal limit of the valves (arrowheads). Black arrows in (D) show the distal intrapericardial limit of the conal myocardium. AVP, atrioventricular plug. Scale bars=1 mm.
