Fig. 4.
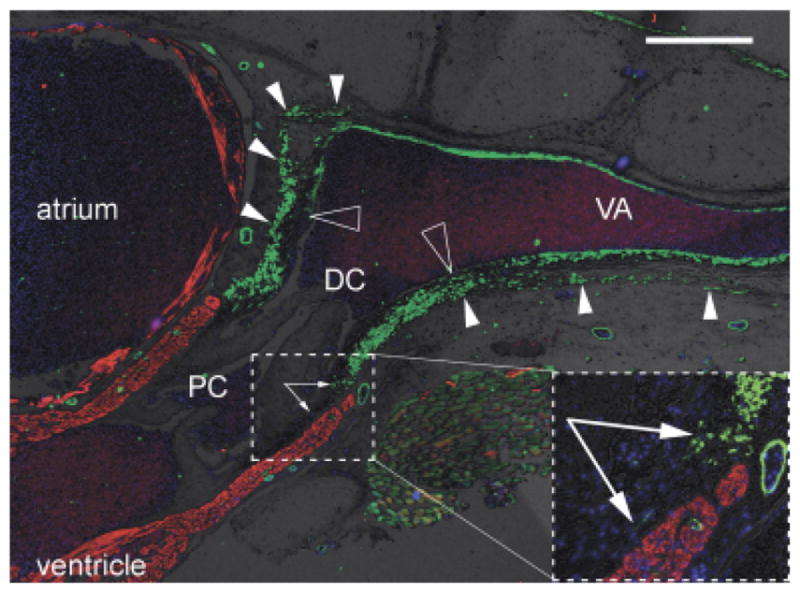
Distinct origin of smooth muscle in distal OFT and ventral aorta? Sagittal section through the heart, outflow tract (OFT) and ventral aorta of a juvenile small-spotted catshark Scyliorhinus canicula, labeled with anti-SMA (green), CH1 (red), and DAPI (blue). Brightfield background shows gross tissue structure. Dorsal to the top, cranial to the right. Large hollow arrowheads show the distal limit of the intrapericardial OFT smooth muscle and, more cranially, the termination of most of the smooth muscle in the tunica media of the ventral aorta. Small arrowheads show where the OFT smooth muscle is continuous with smooth muscle in the pericardium/body wall (most obvious dorsally). Arrows in inset show smooth muscle cells in the subendocardium of the conus arteriosus. Scale bar=500 μm. DC, distal smooth muscle component (bulbus arteriosus); PC, proximal myocardial component (conus arteriosus); VA, ventral aorta.
