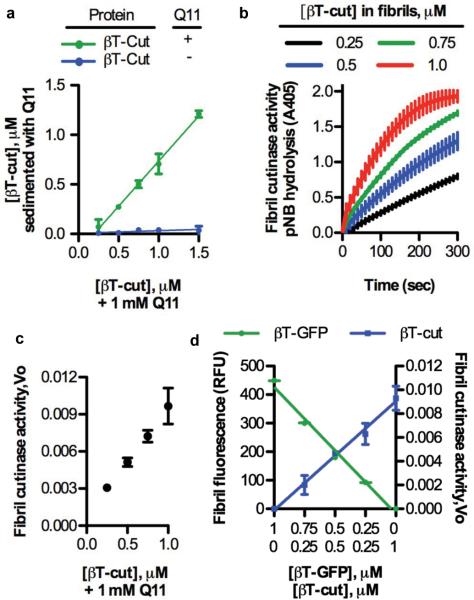
Figure 4. The βTail platform is capable of integrating an enzyme into nanofibers in precise amounts, without loss of enzyme activity.
a) A fusion of βTail and the fungal enzyme cutinase (βTail-cutinase, βT-cut) integrated into Q11 nanofibers over the range of 0.25-1.5 μM in a βTail-dependent manner, as measured by loss of protein from the supernatant following centrifugation. b) Q11 nanofibers assembled in the presence of βTail-cutinase demonstrated cutinase activity, as measured by hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl butyrate (colorless) to p-nitrophenol (yellow). c) Nanofiber cutinase activity was precisely varied by changing the concentration of βTail-cutinase present during Q11 assembly, as determined from the initial velocity of pNB hydrolysis plots in (b). d) βTail- GFP (βT-GFP) and βTail-cutinase (βT-cut) could be mixed into Q11 nanofibers in predictable ratios without loss of activity, as demonstrated by the direct correlation between nanofiber fluorescence or cutinase activity and βTail-GFP or βTail-cutinase concentration, respectively. N = 3, mean ± s.d.