Figure 1. The overall and pooled ORs with a 95% CI for overall and subgroup analysis testing of the association between rs9983 and lupus nephritis.
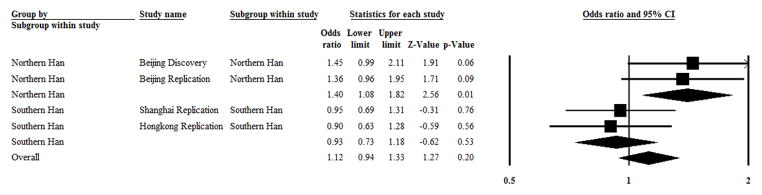
In a subgroup of northern Han Chinese, 878 SLE patients with lupus nephritis, and 556 SLE patients without lupus nephritis as a control were enrolled. I2 = 0 and P = 0.83 in test for heterogeneity, and Z = 2.56 and P = 0.01 in a test for overall effect.
In a subgroup of southern Han Chinese, 535 SLE patients with lupus nephritis and 688 SLE patients without lupus nephritis as a control were enrolled. I2 = 0, P = 0.83 in a test for heterogeneity, and Z = −0.62 and P = 0.53 in a test for overall effect.
Of the total Chinese Han individuals enrolled, 1413 were SLE patients with lupus nephritis and 1244 were SLE patients without lupus nephritis as a control. I2 = 44.7% and P = 0.02 in a test for heterogeneity, and Z = 0.62 and P = 0.54 in a test for overall effect.
A random effects model was used to pool the results because heterogeneity was present.
