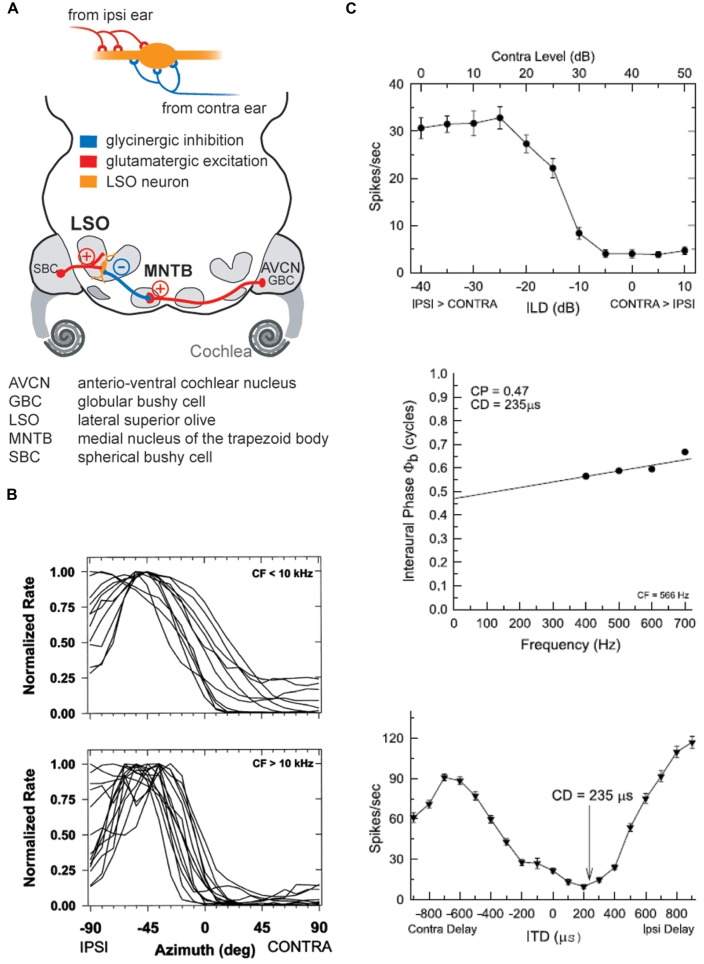
FIGURE 4.
The coincidence mechanism of LSO neurons allows both as ILD and ITD detection. (A) LSO neurons receive excitatory inputs from SBCs in the ipsilateral AVCN and inhibitory inputs from the MNTB that is innervated from by GBCs from the contralateral AVCN. (B) The spatial tuning functions of LSO neurons take a hemispheric shape with the slope of the functions crossing frontal azimuthal positions. Upper and lower panels show normalized tuning functions for LSO neurons in cat with CFs below and above 10 kHz, respectively, recorded under virtual acoustic space stimulation that incorporates the HRTFs. Re-printed with permission from Tollin and Yin (2002). (C) Low CF neurons in the LSO are both ILD and ITD sensitive: upper panel shows ILD tuning function of a cat LSO neuron (CF = 566Hz), while the lower two panels illustrate the ITD-sensitivity of the same neuron. Note that the characteristic delay (CD) for this neuron, i.e., the delay of coincidence of excitatory and inhibitory inputs, results in a minimal response rate. Re-printed with permission from Tollin and Yin (2005).