Figure 2. C. elegans miRNA:Targets (3,600) Derived from Chimeras Reflect Endogenous miRNA Targeting.
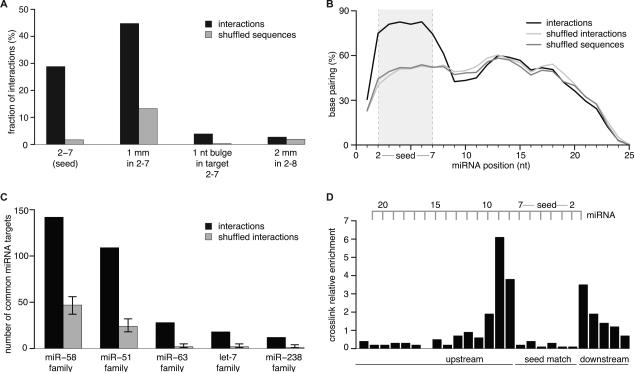
(A) Target RNAs were analyzed for complementarity to the seed region of their ligated miRNAs. ~80% of interactions possess the tested complementarities. Shuffled sequences (dinucleotides in target sequences are permuted) served as control. mm = mismatch Mismatches were broadly distributed over all types of nucleotides, including G:U.
(B) Hybridization profile summarized over all interactions. The predicted frequency of a miRNA position to be base paired is plotted along the miRNA length. Duplex structures of miRNA:targets were predicted by RNAhybrid allowing G:U pairing. Shuffled sequences (dinucleotides in target sequences are permuted) and shuffled interactions (targets are swapped between miRNAs) served as control.
(C) Target sites derived from miRNA-chimeras are more often found ligated to miRNAs of the same family than expected by chance (p < 0.0001). Shuffling target sites between miRNA families served as control.
(D) Local frequency of crosslink-induced T to C conversions in target RNAs from interactions with a perfect 2-7 seed match (normalized to local thymidine frequency). Nucleotides hybridized to the seed of the miRNA are strongly indisposed to crosslink with the protein. See also Figure S2.