Figure 1.
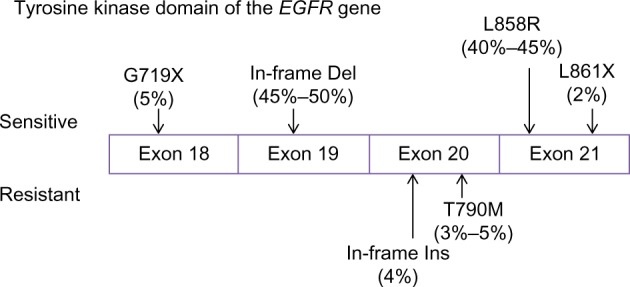
Tumor-driving mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor).
Notes: The most common EGFR mutations are in-frame deletions (Del) in exon 19 (45%–50%), which remove four high conserved amino acid residues (the LREA motif) of EGFR, and a point mutation in exon 21 (40%–45%), causing substitution of an arginine by a leucine (L858R). Both of them are sensitive to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Other TKI-sensitive mutations include point mutations such as G719X in exon 18 and L861X in exon 21. In contrast, patients harboring a T790M point mutation or in-frame insertions (Ins) in exon 20 are less sensitive to TKIs. T790M mutation is also an important mechanism in acquired TKI resistance. Data were derived from previous reports.54,59,60,76,77
