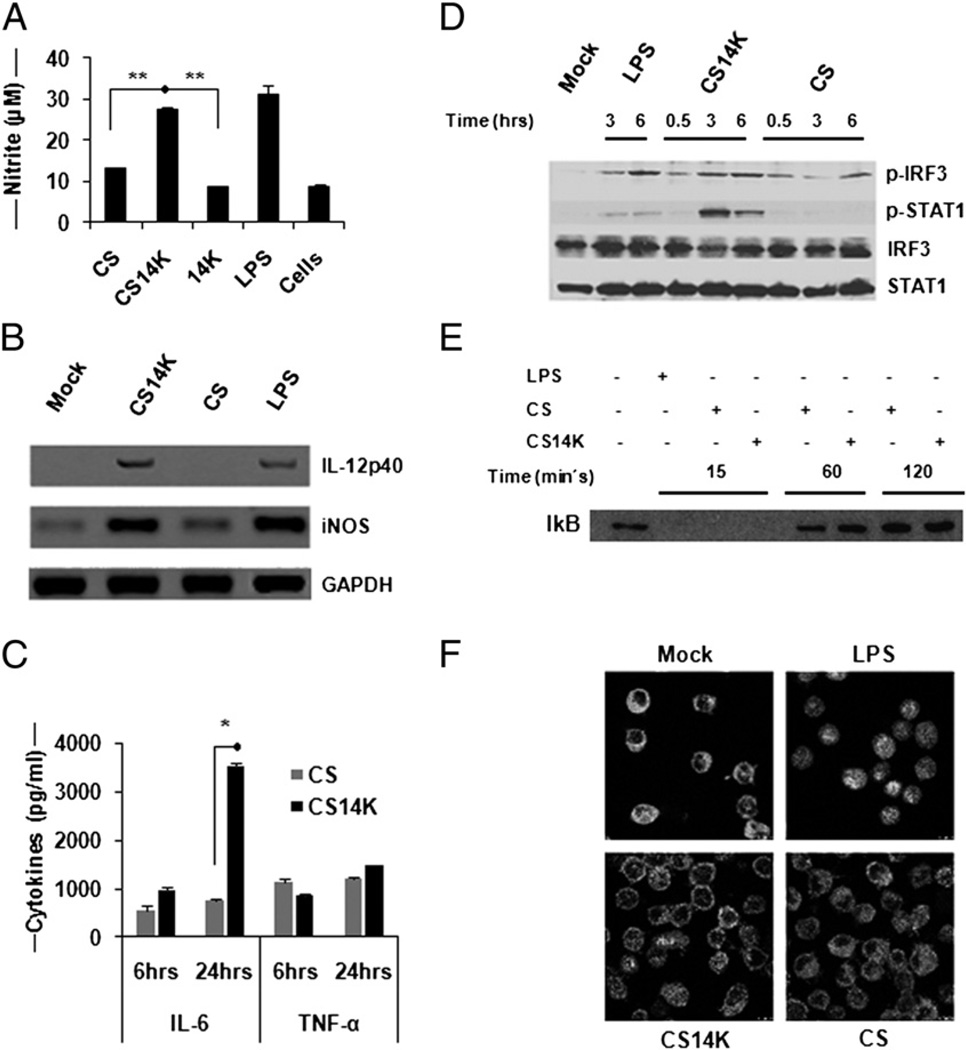
FIGURE 2.
Modulation in innate immune sensing of CS14K by macrophages: fusion protein can activate innate sensing in macrophages. THP-1 or J774 macrophage cells were stimulated with 5 µg/ml proteins or as positive control with 1 µg/ml LPS. (A) Induction of NO by proteins in macrophages. Nitrite accumulation in the supernatant was determined after 48 h protein treatment in J774. (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of NO and IL-12p40 expression. RNA was extracted and the corresponding cDNA was obtained as mentioned in Materials and Methods. Proportionate volume of amplified DNA was run on 8% agarose gel. (C) Cytokine analysis by Luminex assay. Supernatants were collected after 6 and 24 h treatment. Cytokine levels in the supernatant were measured by Luminex. (D) CS14K induces IRF-3 and STAT-1 phosphorylation: 2 × 106 THP-1 cells were stimulated with proteins, following which the samples were collected at different time intervals and probed with phospho-Abs against IRF-3 and STAT-1. Normalization was carried out using total STAT-1 and IRF-3 Abs (1:1000). (E and F) Proteins inhibit NF-κB activation: proteins block the movement of p65 (mouse anti-p65 NF-κB Ab p65, 1:500) into the nucleus in J774 macrophages inspite of IkB degradation. Images were acquired at ×63 objective magnification. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e. of triplicate observation and are representative of two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005.