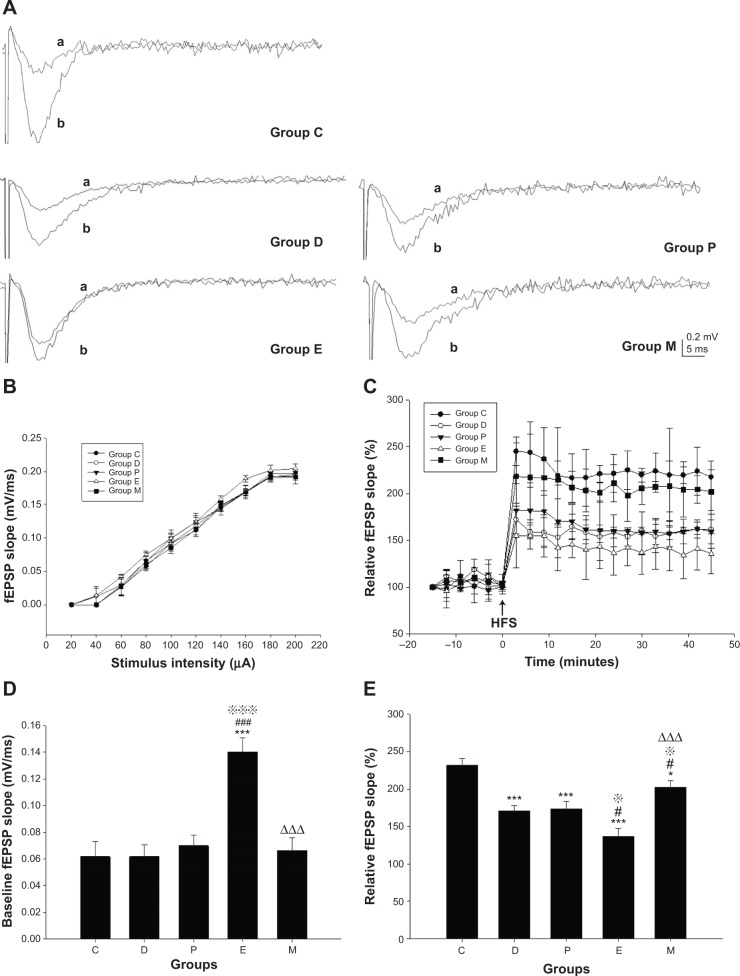
Figure 5.
LTP in the CA1 region in hippocampus of rats after ECS (or MECS) treatment.
Notes: Original traces of fEPSP in each group (A); input/output curves in each group (B); the induction and maintenance of LTP (C); baseline fEPSP slope (D); relative fEPSP slope (E). Data are presented as the mean ± SE; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 versus group C; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 versus group D; P<0.05, P<0.001 versus group P; ΔΔΔP<0.001 versus group E. C represents control rats; D represents CUMS-pretreated rats that received sham ECS with normal saline pretreatment; P represents CUMS-pretreated rats that received sham ECS with propofol pretreatment; E represents CUMS-pretreated rats that received ECS with normal saline pretreatment; M represents CUMS-pretreated rats that received ECS with propofol pretreatment; n=5 in each group. aoriginal trace of baseline fEPSP; boriginal trace of fEPSP after HFS.
Abbreviations: CUMS, chronic unpredictable mild stresses; ECS, electroconvulsive shock; fEPSP, field excitatory postsynaptic potential; HFS, high frequency stimulation; LTP, long-term potentiation; MECS, modified ECS; SE, standard error.