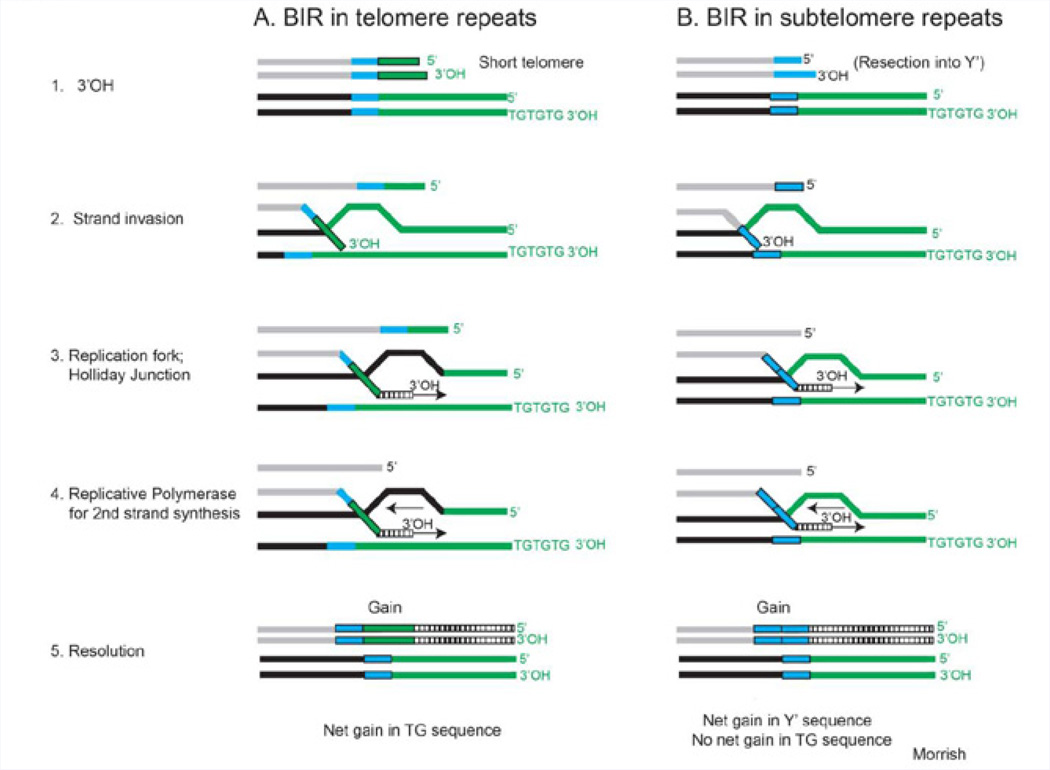
Figure 1. Break-induced replication.
Shown are models of break-induced replication based on studies in yeast (54). A. For Type II survivors, the 3’-OH of a short telomere (green) strand invades into another telomere repeat. This sequence can be on the other homolog or on a different chromosome. Strand invasion generates a replication fork and a Holliday junction. Conventional DNA polymerases are used to synthesize both strands, followed by resolution of the Holliday junction. BIR that initiates in the telomere repeat will result in a net gain of telomere sequence. B. For Type I survivors, BIR in subtelomere repeats occurs when telomere shortening proceeds into a Y’ (blue) repeat. BIR that is initiated within the subtelomeres results in a net gain in Y’ sequence.