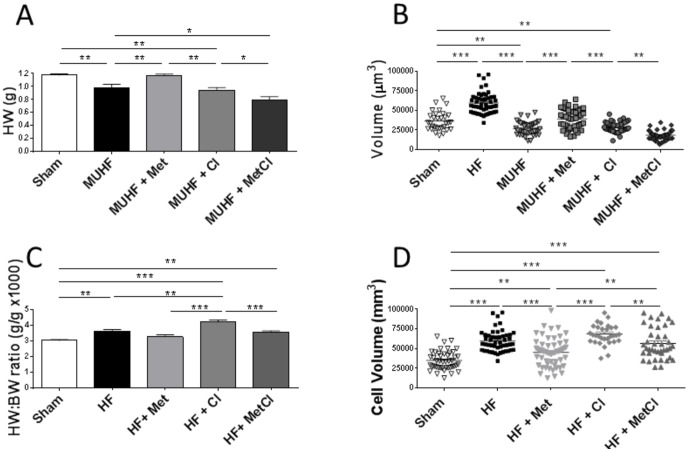
Figure 3. Effect of Cl, Met and combined MetCl treatment on heart weight (HW) (A) and cardiomyocyte volume measured using confocal microscopy (B) during unloading (MUHF).
Prevention of MU-induced cardiac and cardiomyocyte atrophy is achieved by Met and not Cl, with combined MetCl therapy increasing atrophy. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, (HW and cardiomyocyte volume data acquired from 8 and 4 hearts per group, respectively). Effect of Cl, Met and combined MetCl therapy on heart weight∶body weight ratio (HW∶BW) (C) and cardiomyocyte volume (D). HF-induced cardiac hypertrophy was enhanced by Cl therapy but this effect disappeared during combined MetCl therapy. HF-induced myocyte hypertrophy was partially attenuated by Met, but this effect was lost during combination MetCl therapy (HW and cardiomyocyte volume data acquired from 8 and 4 hearts per group, respectively).