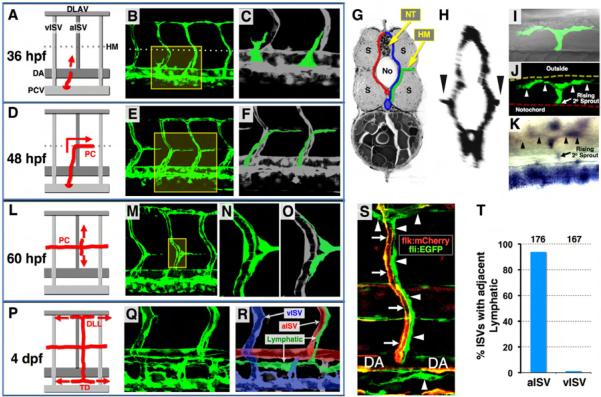
Figure 1. Anatomy and assembly of the trunk lymphatic network in the developing zebrafish.
(A, D, L, and P) Diagrams illustrating successive steps in trunk lymphatic network assembly at different developmental stages (red, developing lymphatics; red arrows, their growth direction). (B, E, M, and Q) Confocal images of the vasculature in Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 animals at each stage (yellow boxes, magnified areas shown to the right). (C, F, N, and O) Magnified views of the boxed portions of the images to the left (green, developing lymphatic vessels except N). (R) Color-coded image of Q (green, lymphatic vessels; red, arterial BV; blue, venous BV). (G) Cross-sectional diagram illustrating lateral growth of lymphatic progenitors (green) toward the superficial HM (red, arterial BV; blue, venous BV; No, notochord; NT, neural tube; S, somites). (H) Cross-sectional reconstruction (rotated 90 degrees) of confocal stacks used in E (arrowheads, vascular spouts extending laterally along the HM). (I and J) Dorsal view confocal/DIC (I) and confocal only (J) images of a single branching PC sprout (arrowheads) in the superficial HM of a 60 hpf Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 larva. (K) Dorsal view image of a branching PC sprout (arrowheads) in the superficial HM of a 56 hpf larva WISH-stained for prox1. (S) Confocal image of an aISV (red/yellow, arrows) with a co-aligned ISLV and other developing lymphatics (green, arrowheads) in a 3 dpf Tg(flk:mCherry), Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 double transgenic animal. (T) Quantification of aISV and vISV (determined by observing vessels using confocal microscopy at 5 dpf) with a co-aligned ISLV. The total number of aISV or vISV counted is shown above each bar.