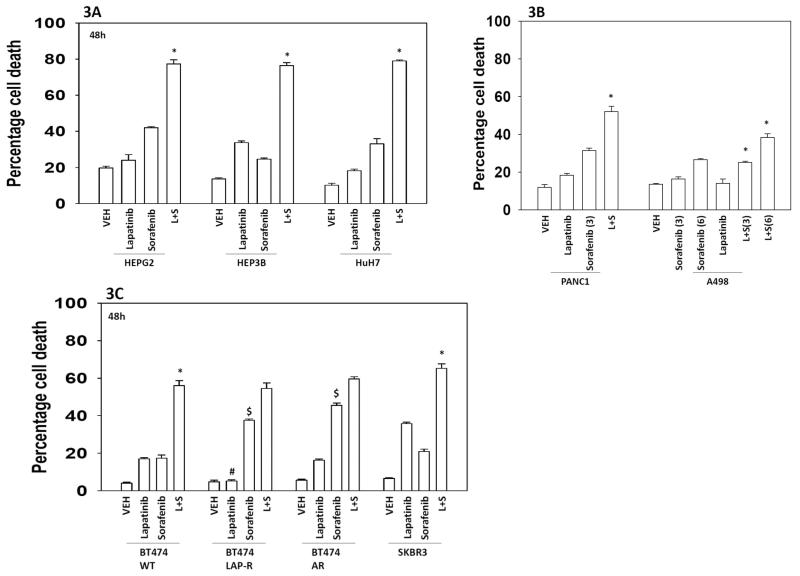
Figure 3. Sorafenib and lapatinib interact to kill multiple tumor types.
(A) HEPG2 / HEP3B / HuH7 hepatoma cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO), sorafenib (6.0 μM) and/or lapatinib (2.0 μM) as indicated. Cells were isolated 24h after exposure and viability determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3, +/− SEM) *p < 0.05 greater than vehicle control. (B) PANC1 pancreatic and A498 renal carcinoma cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO), sorafenib (3.0, 6.0 μM as indicated) and/or lapatinib (2.0 μM) as indicated. Cells were isolated 24h after exposure and viability determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3, +/− SEM) *p < 0.05 greater than vehicle control. (C) Breast cancer cells: SKBR3; parental wild type BT474; lapatinib-resistant BT474; anoikis resistant BT474; were treated with vehicle (DMSO), sorafenib (6.0 μM) and/or lapatinib (2.0 μM) as indicated. Cells were isolated 24h after exposure and viability determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3, +/− SEM) *p < 0.05 greater than vehicle control; #p < 0.05 less than corresponding value in wild type BT474 cells; $ p < 0.05 greater than corresponding value in wild type BT474 cells.