Fig. 4.
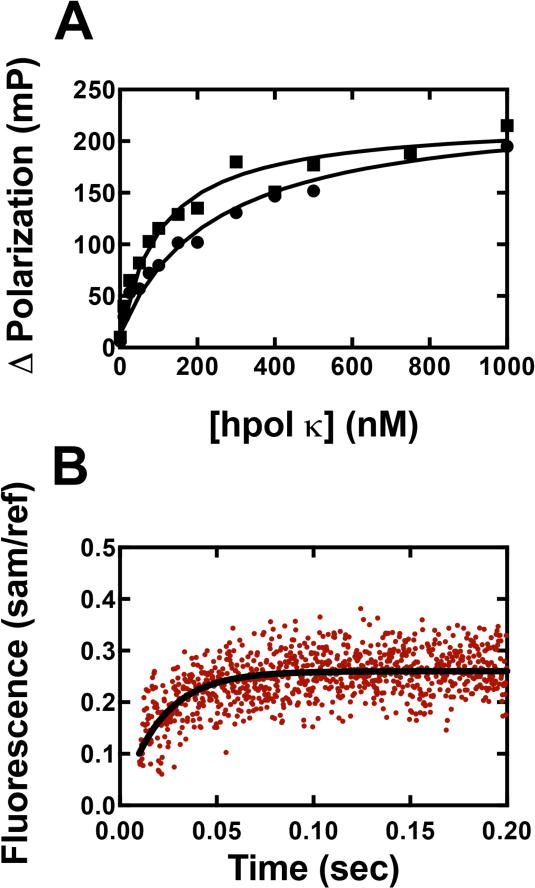
Determination of Kd,DNA and koff,DNA. (A) Fluorescence anisotropy experiments for determination of Kd,DNA. A FAM-labeled 24-/36-mer duplex (2 nM) was incubated with varying concentrations of hpol κ or Y50W (0 to 1 μM), and fluorescence polarization was measured. All titrations were performed in 50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.5) containing 10 mM potassium acetate, 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 0.1 mg mL−1 BSA. Results were analyzed using eq. 4 and eq. 5 to obtain 100 (± 20) μM and 240 (± 30) for Y50W (■) and WT hpol κ (●), respectively. (B) Fluorescence change (red dots) measured (stopped-flow) upon mixing a pre-formed complex of WT hpol κ (2 μM):FAM-labeled 24-/36-mer duplex (0.4 μM) with a regular 24-/36-mer duplex (2 μM) (used as a trap). Experiments were performed in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.8 at 25 °C) containing 50 mM NaCl and 5 mM DTT. The excitation wavelength was 485 nm with an emission wavelength 515 nm cutoff (long-pass) filter (Newport, Irvine, CA) and a 1 mm slit width. The resulted fluorescence change was fitted to a single exponential equation (fit shown with black curve) to obtain koff,DNA = 48 (±2) s−1.
