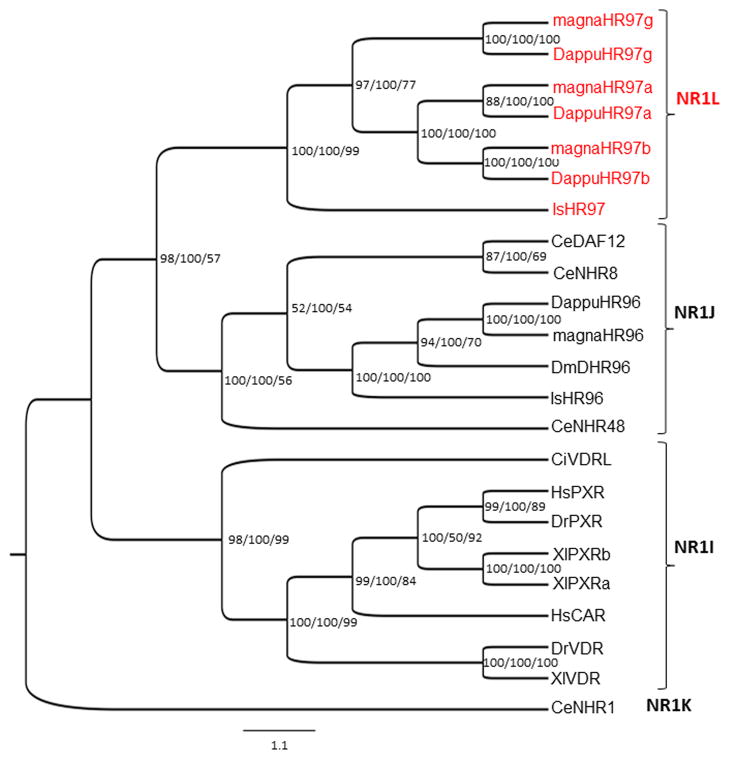
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analysis of the NR1L nuclear receptor group.
Bayesian Inference, Maximum Parsimony, and Neighbor-Joining were used to determine the relationship of the NR1L (HR97) group of NRs to the related NR1J and NR1I groups. NRs from several different species were analyzed following alignment of their conserved C (DBD) and E (LBD) domains using Bayesian Inference, Maximum parsimony and Neighbor-Joining methods. The Bayesian tree is shown with posterior probabilities from the Bayesian tree, and bootstrap support values (frequency of occurrence) from the Neighbor-Joining and Maximum Parsimony trees provided in order from left to right, respectively as confirmatory analysis of the Bayesian analysis at each node. CeNHR1 (NR1K1) was chosen as the outgroup. Abbreviation of species names are as follows: magna=Daphnia magna, Dappu=Daphnia pulex, Is=Ixodes scapularis, Ce=Caenorhabditis elegans, Dm=Drosophila melanogaster, Ci=Ciona intestinalis, Dr=Danio rerio, Hs=Homo sapiens, Xl=Xenopus laevis. Accession numbers of the analyzed NRs are provided in Additional File 1.