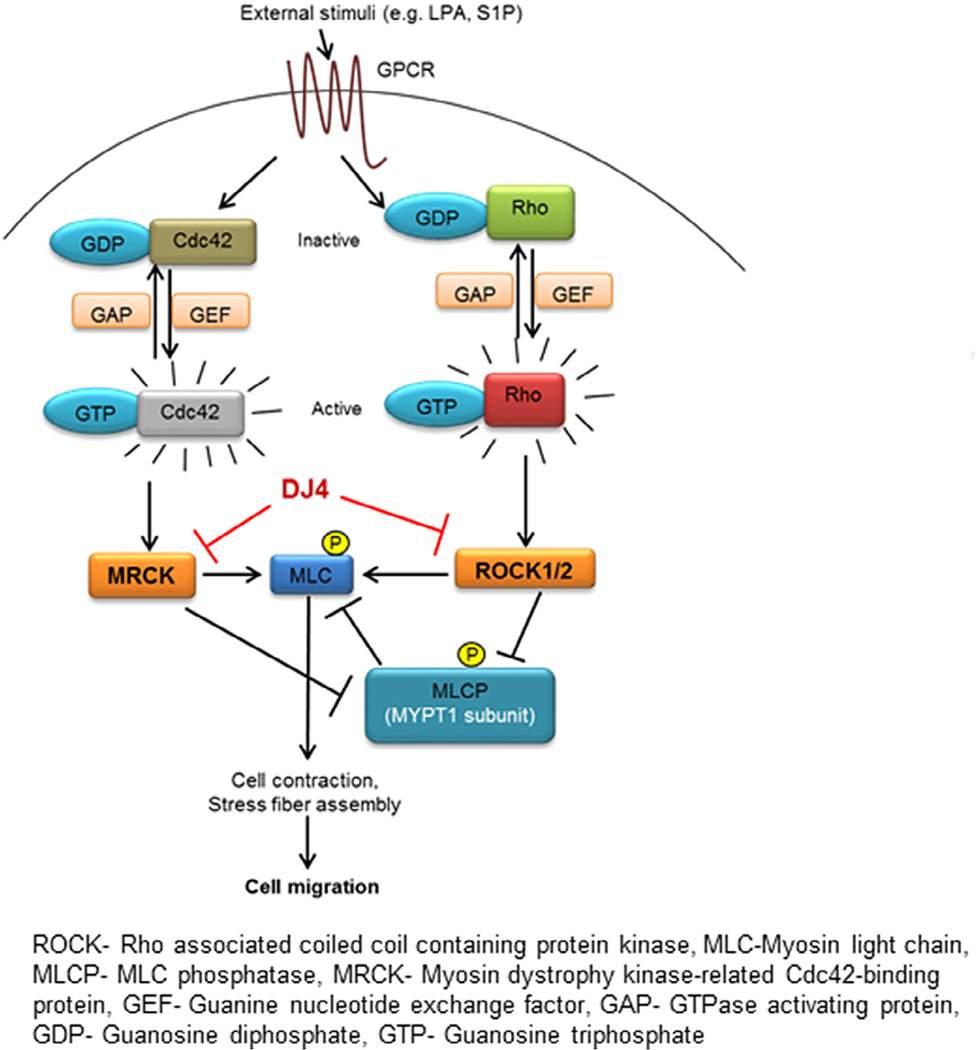
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of the effects of DJ4 on migration/invasion. Ligation of G-protein coupled receptors activates Rho and Cdc42 signaling to activate ROCK1/2 and MRCKα/β, respectively, resulting in formation/contraction of stress fibers and cellular migration. DJ4 through inhibition of ROCK1/2 and MRCKα/β blocks the phosphorylation of MLC at Ser19 resulting in disruption of stress fiber formation. Simultaneously, by inhibiting ROCK1/2 and MRCKα/β activity, DJ4 also blocks the inactivating phosphorylation of MYPT1 (Thr696), the regulatory subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) resulting in the activation of MLCP. Active MLCP further enforces the dephosphorylated state of MLC at Ser19. Thus the DJ4 mediated disruption of stress fiber formation inhibits cellular migration/invasion.