Fig. 6.
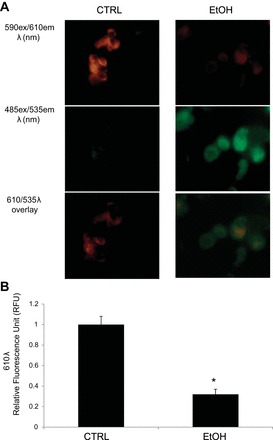
Mitochondrial membrane potential. Chronic alcohol ingestion significantly decreased membrane polarization in mitochondria derived from rat alveolar type 2 cells as measured from JC-1 labeling. A: chronic alcohol consumption results in predominantly green JC-1 fluorescence (due to low mitochondrial membrane potential; right), whereas the dye aggregates and fluoresces red under control conditions (due to high mitochondrial membrane potential; left). Bottom: overlay of red and green emission profiles of JC-1 labeled cells. B: average 610 λ excitation values of JC-1 labeled cells performed in triplicates from 6 animals (*P < 0.05) indicating that chronic ethanol consumption significantly decreases mitochondrial membrane potential.
