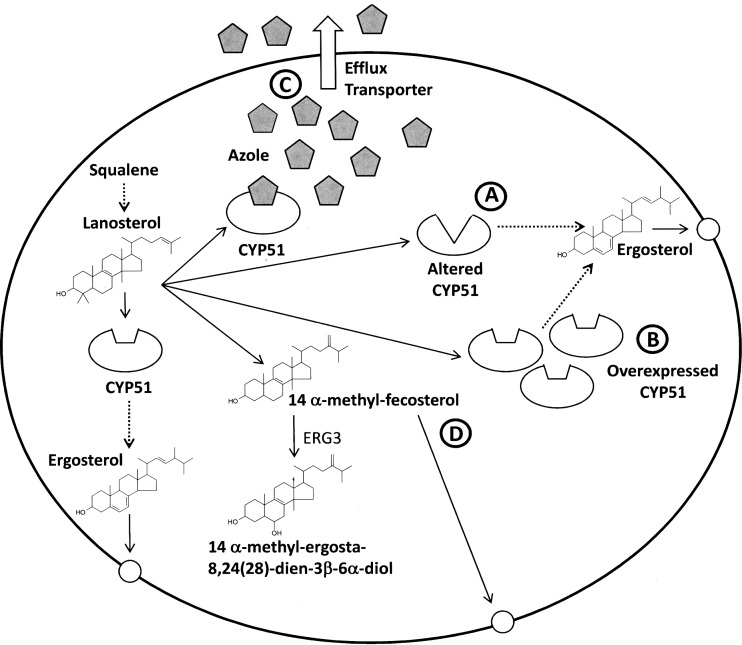
Fig. 2.
Azole resistance mechanisms in C. albicans. CYP51 is an essential step in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, which is required for membrane stability and functionality. Azoles inhibit CYP51 causing the accumulation of 14 α-methyl-ergosta-8,24(28)-dien-3β-6α-diol. Resistance to azoles can occur through a an altered CYP51 (point mutations), b overexpression of CYP51, c overexpression of efflux transporters and d null mutation of ERG3 which blocks the synthesis of 14 α-methyl-ergosta-8,24(28)-dien-3β-6α-diol, resulting in the accumulation of 14 α-methyl-fecosterol which is capable of supporting membrane function