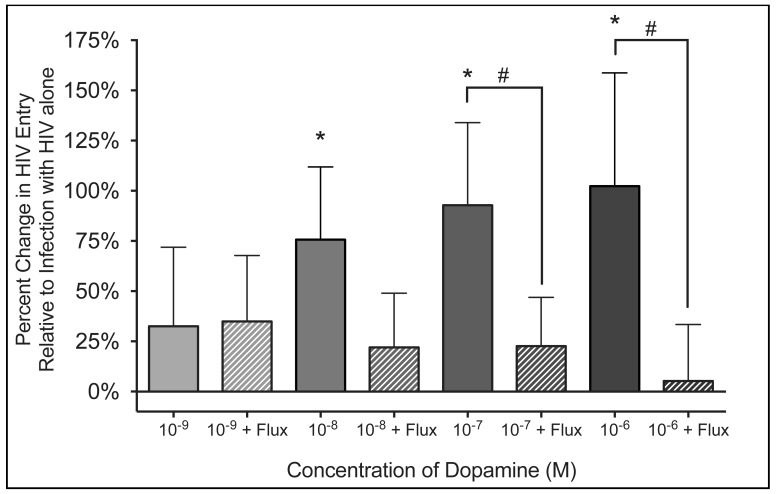
Figure 4. Activation of dopamine receptors required for the dopamine-mediated increase in HIV entry.
Macrophages were pretreated with the pan-dopamine receptor (DR) antagonist flupenthixol (flux, 106 M) and then MOI 0.01 β-lac HIV was added concurrently with either 109, 108, 107 and 106 M dopamine. As controls, both vehicle treated and flupenthixol treated cells were infected with HIV alone. Solid columns represent infections in the presence of dopamine, while hatched columns to the right of each solid column of the same color represent infections in presence of an identical concentration of dopamine as well as flupenthixol. There was a significant increase in viral entry into macrophages infected with HIV the presence of 108, 107 and 106 M dopamine (n = 7 for all concentrations of dopamine, * p < 0.05 vs. HIV only). This increase was blocked by flupenthixol treatment, and entry was significantly reduced in the presence of 107 and 106 M dopamine (n = 7, # p < 0.05 vs. identical concentration of dopamine without flupenthixol).