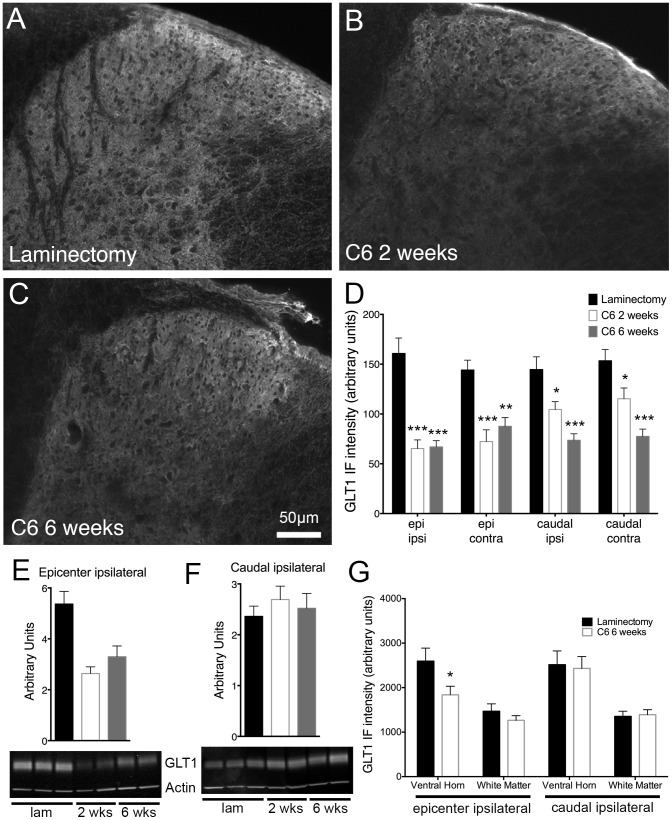
Figure 7. Cervical contusion SCI resulted in decreased astrocyte GLT1 expression in the dorsal horn.
Immunohistochemical analysis revealed a decrease in GLT1 protein expression two (B) and six weeks (C) after cervical contusion SCI compared to laminectomy (A). This downregulation of the glutamate transporter was seen in the superficial dorsal horn on both sides of the spinal cord both at the injury site and caudal to the injury (D). Immunoblots of spinal cord tissue also showed a significant loss of GLT1 expression on the ipsilateral side at both time points following injury. However, this difference was seen only at the epicenter (E) and not caudal to the injury (F). Representative immunoblots are shown for each region (E–F). Analysis of GLT1 levels in regions of the spinal cord other than the superficial laminae at six weeks after injury reveal a loss of GLT1 expression in the ventral horn at the epicenter with no changes caudal to the injury (G). IF = immunofluorescence; epi = epicenter; ipsi = ipsilateral; contra = contralateral; lam = laminectomy; * = p<0.05; ** = p<0.01; *** = p 0.001.