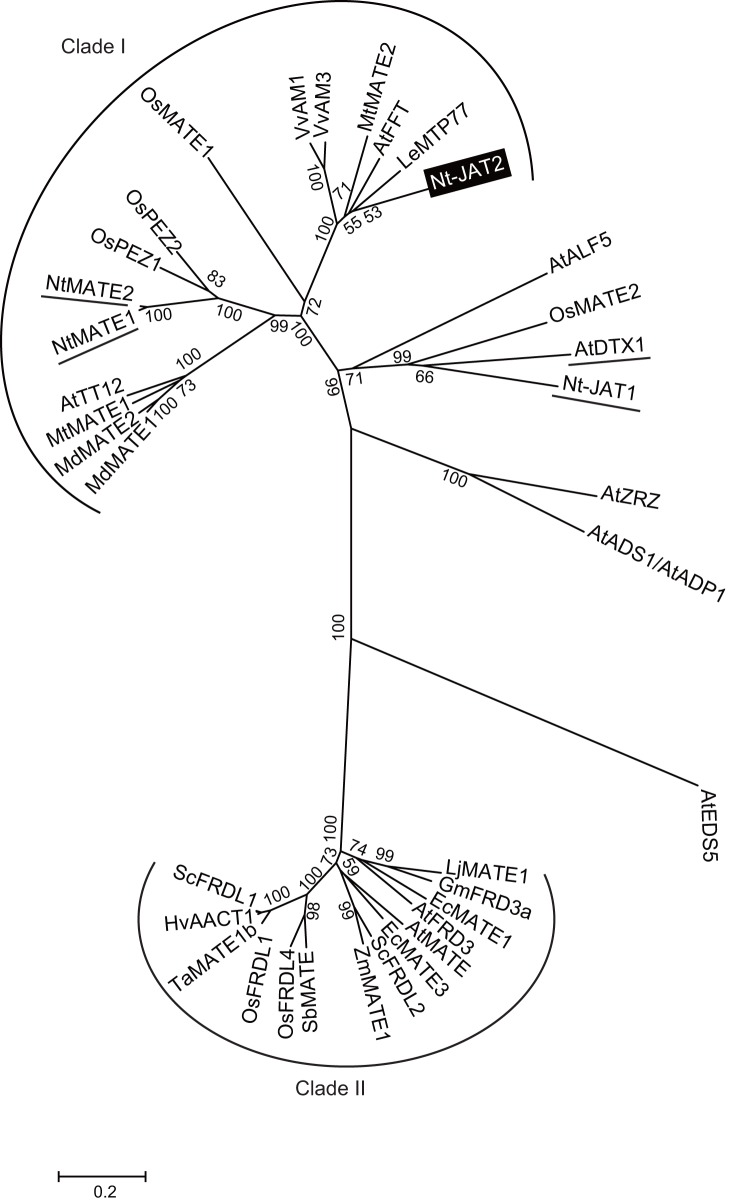
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship of plant MATE family members.
Amino acid sequences of MATE members were aligned with ClustalW and subjected to phylogenetic analysis using MEGA6 software [43] with the neighbor-joining algorithm. Numbers on the branches represent bootstrap values. Proteins that transport alkaloids as substrates are underlined. The scale bar shows the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Most proteins belonging to clade I transport secondary metabolites, such as epicatechin 3′-O-glucoside, apigenin 7-O-glucoside, malvidin 3-p-coumaroylglucoside, nicotine, and protocatechuic acid; whereas almost all Clade II proteins transport citrate. Arabidopsis MATE members are: AtADS1/AtADP1, At4g29140; AtALF5, At3g23560; AtDTX1, At2g04070; AtEDS5, At4g39030; AtFFT, At4g25640; AtFRD3, At3g08040; AtMATE, At1g51340; AtTT12, At3g59030; AtZRZ/AtBCD1, and At1g58340. MATE members of other plant species and their accession numbers are: EcMATE1 (Eucalyptus camaldulensis), BAM68465; EcMATE3, BAM68467; GmFRD3a (Glycine max), ACE89001; HvAACT1 (barley), BAF75822; LeMTP77 (tomato), AAQ55183; LjMATE1 (Lotus japonicus), BAN59993; MdMATE1 (Malus domestica), ADO22710; MdMATE2, ADO22712; MtMATE1 (Medicago truncatula), ACX37118; MtMATE2, ADV04045; Nt-JAT1 (Nicotiana tabacum), CAQ51477; NtMATE1, BAF47751; NtMATE2, BAF47752; OsFRDL1 (Oryza sativa), BAG95121; OsFRDL4, BAL41687; OsMATE1, Os03g08900; OsMATE2, Os05g48040; OsPEZ1, AK243209; OsPEZ2, Os03g0572900; SbMATE (Sorghum bicolor), ABS89149; ScFRDL1 (rye), BAJ61741; ScFRDL2, BAJ61742; TaMATE1b (Triticum aestivum), AFZ61900; VvAM1 (Vitis vinifera), ACN91542; VvAM3, ACN88706; and ZmMATE1 (Zea mays), ACM47309.