Figure 4. Transformation-Competent Oncoprotein HPV16-E7 Inhibits PKM2 Tetramerization and Promotes K433 Acetylation.
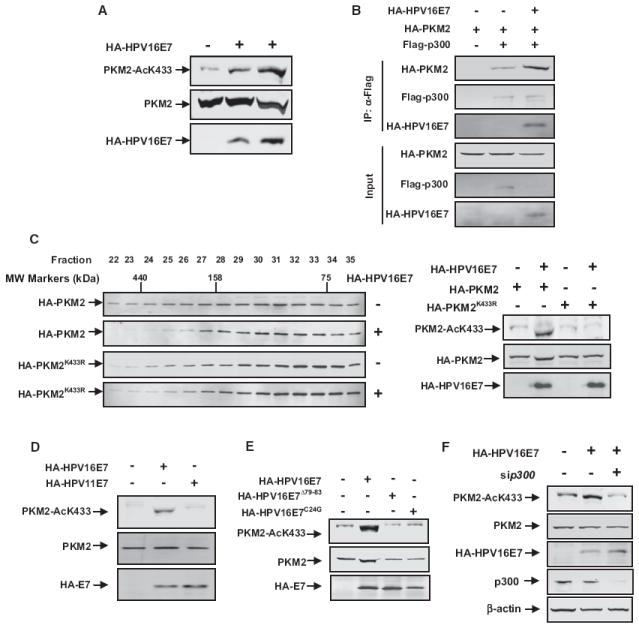
(A) HPV16-E7 promotes K433 acetylation of PKM2. Cell lysates were prepared from 3T3 cells transfected with empty vector or increasing amounts of HPV16-E7, followed by western analysis of total and K433-acetylated PKM2.
(B) HPV16-E7 promotes the interaction between PKM2 and p300. 3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. p300-PKM2 interaction was examined by IP-western analysis.
(C) HPV16-E7 prevents tetramerization of wild-type, but not K433R mutant PKM2. Cell lysates were prepared from 1 × 107 cells cotransfected with empty vector or HPV16-E7 with either wild-type or K433R mutant PKM2, separated by gel filtration, followed by western analysis for PKM2 protein and K433 acetylation.
(D) High-risk HPV16-E7, but not low-risk HPV11-E7, promotes K433 acetylation. 3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. The expression of individual proteins and K433 acetylation of PKM2 were determined by western analysis.
(E) Transformation-deficient HPV16-E7Δ79-83 and HPV16-E7C24G mutants are unable to promote K433 acetylation. 3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. The expression of individual proteins and K433 acetylation of PKM2 were determined by western analysis.
(F) Small interfering p300 (si-p300) blocks HPV16-E7-induced K433 acetylation of PKM2. 3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and oligos, and PKM2 acetylation at K433 was determined by western blot. See also Figure S3.
