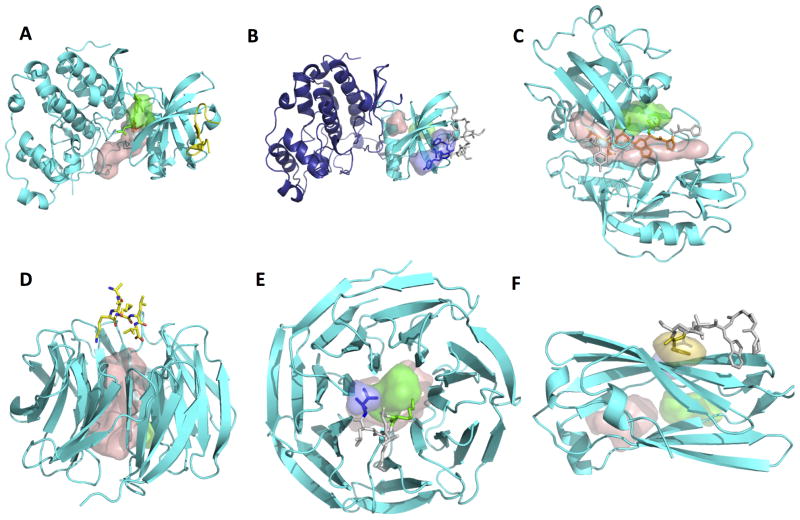
Figure 1. Examples of predictions of peptide binding sites using PeptiMap.
The same color-coding scheme is used in all figures: The receptor is shown as a cartoon colored in cyan, while the different predicted sites are shown in surface representation (top-ranking site – wheat; site 2 – green; site 3 - dark blue). The peptide is shown in stick representation and colored according to the predicted binding sites (residues that do not contact any predicted site are in light grey). Pdb IDs of the apo and bound structures are indicated in parentheses. Predictions were made on the apo structures; bound structures are for validation purposes only.
(A, B) Mapping on single domains improves peptide binding site prediction on ck2 kinase (apo: pdb ID 3BQC chain A): (A) mapping on the full structure identifies merely a known ligand binding site (pdb ID 3U4U), while (B) mapping on the n-terminal kinase domain only identifies the peptide binding site (pdb ID 4IB5; the transferase domain not mapped here is shown in dark blue). This highlights how implementation of segmentation into single domains may improve in particular peptide-binding site predictions (while small ligands can be identified also on the full structure).
(C) Example of accurate PeptiMap prediction of the peptide binding site covering a substantial part of the peptide: Endothiapepsin peptide binding site prediction identifies the peptide binding site of all but one residue (apo: pdb ID 4APE chain A; bound: 1ER8). (D, E) Masking of internal ligand binding sites improves peptide binding site prediction on coatomer b subunit. (D) In the original prediction, mapping of the receptor structure (pdb ID 3MKQ chain A) identifies mainly peptide-inaccessible sites within the whole of the WD40 domain, but not the peptide binding site (pdb ID 4J73). (E) When entrance into the inner cavity is blocked, PeptiMap identifies correctly the location of the peptide-binding site. (F) Example of target failed by Peptimap. In case of the AP-2 complex subunit alpha (CATH domain 2.60.40.1030; pdb ID 1B9K), the peptide binding site (from pdb ID 2VJ0) is not identified by the top 3 predictions, only by prediction ranked 4th (in yellow).