Figure 9. Proposed mechanisms for antidepressant-induced modulation of astroglial cytokine production in a transgenic model of MSA.
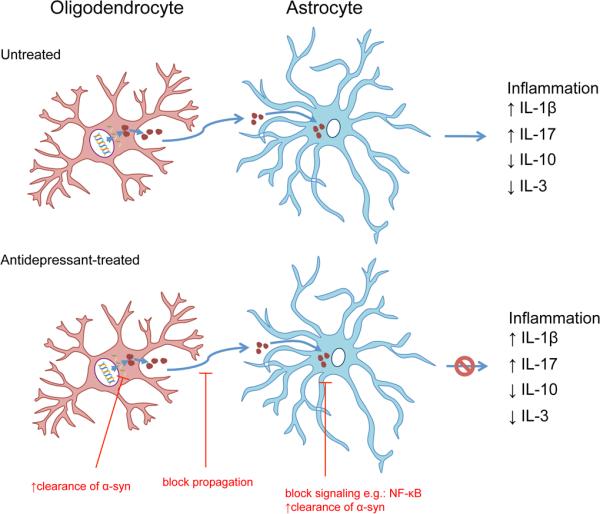
Our results suggest that (A) in the MBP1-hα-syn transgenic mice, oligodendrocytes express the human α-syn transgene and synthesize high levels of α-syn protein. α-syn oligomerizes (red spheres) and it might be released to the extracellular environment. Astrocytes might incorporate extracellular α-syn and accumulate it intracellularly, leading to an imbalance in the production of cytokines. (B) In the antidepressant-treated MBP1-hα-syn transgenic mice, antidepressants might regulate cytokine production by several mechanisms: increasing oligodendroglial clearance of α-syn, blocking release and/or internalization of α-syn, and/or increasing astroglial clearance of α-syn. The reduction in astroglial α-syn accumulation, together with regulation of molecular mechanisms involving transcription factors such as NF-κB, might modulate the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, leading to reduced neuroinflammation.
