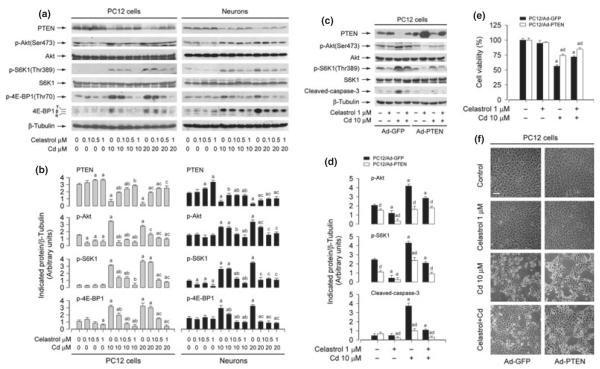
Fig. 6.
Celastrol blocks Cd-induced neuronal cell death by preventing cadmium (Cd) from reducing phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) expression and activating Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. (a) Pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells and primary neurons were pre-treated with celastrol (0–1 μM) for 1 h, and then exposed to Cd (10 and 20 μM) for 12 h, following by western blot analysis with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Celastrol inhibited Cd-induced phosphorylation of Akt, S6K, and 4E-BP1, with a concomitant restoring of Cd-down-regulated PTEN dose-dependently. (c, e, f) PC12 cells, infected with Ad-PTEN-wt or Ad-GFP (as control), were pre-treated with celastrol (1 μM) for 1 h, and then exposed to Cd (10 μM) for 12 h (for western blotting) or 24 h [for 3-(4,5-dimethylazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolim bromide (MTT) assay or morphological analysis], followed by (c) western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies, (e) cell viability evaluation using MTT assay, or (f) morphological analysis using a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U inverted phase-contrast microscope (200×) equipped with a digital camera. Scale bar: 100 μm. For (a) and (c), similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments, and blots for PTEN, p-Akt, p-S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), p-4E-BP1, cleaved-caspase-3 were semi-quantified (b, d). Results are presented as mean ± SE; n = 3–5. ap < 0.05, difference with control group; bp < 0.05, difference with 10 μM Cd group; cp < 0.05, difference with 20 μM Cd group; dp < 0.05, Ad-PTEN group versus Ad-GFP group.