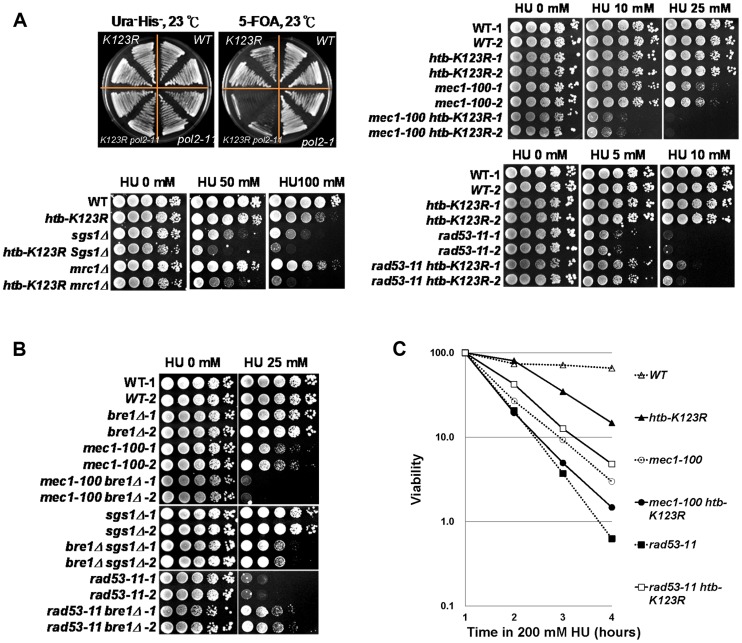
Figure 4. The Bre1-H2Bub pathway genetically interacts with components of the intra-S-phase checkpoint.
(A) H2Bub functions in parallel with DNA polymerase (pol2-11) and intra-S-phase checkpoint cascades (Mec1, Sgs1, and Mrc1). WT and pol2-11 cells carrying HTB1 or the htb1-K123R allele on a HIS3 vector were transformed with HTB1 on a URA3 vector. The strains containing both URA3 and HIS3 (CFK2000, CFK2002, CFK2004, and CFK2006) were streaked onto 5-FOA plates to select for cells lacking H2Bub (htb1-K123R). Ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted onto YPD plates in the absence or presence of different doses of HU at 30°C (WT (CFK1204, CFK2352, and CFK2414), htb-K123R (CFK1231 and CFK2416), mec1-100 (CFK2346), sgs1Δ (CFK1447), mrc1Δ (CFK1444), rad53-11 (CFK2347), and double mutants (CFK2356, CFK1453, CFK1450, and CFK2358)). (B) The H2B ubiquitin E3 ligase, Bre1, functions in parallel with intra-S-phase checkpoints under HU stress. Ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains (WT (CFK2351), bre1Δ (YMW093), mec1-100 (CFK2346), mec1-100 bre1Δ (YMW095), sgs1Δ (CFK2371), bre1Δ sgs1Δ (CFK2373), rad53-11 (CFK2347), and rad53-11 bre1Δ (CFK2378)) were spotted onto YPD plates with and without HU as described in (A). (C) The response of double mutants of htb-K123R and mec1-100 or rad53-11 to acute exposure to HU. Logarithmically-growing cells were treated with 0.2M HU as described in Fig. 1A.