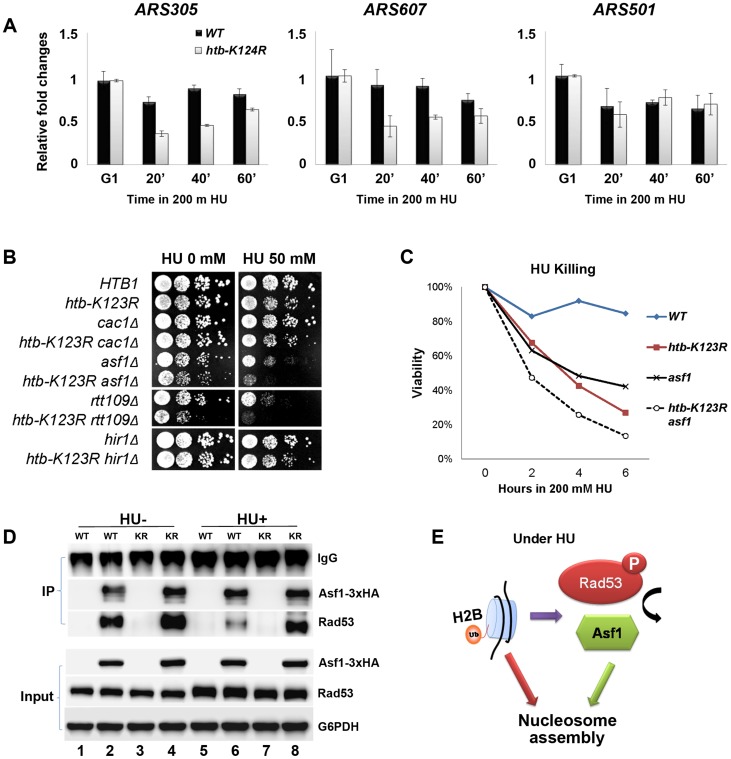
Figure 7. H2Bub promotes chromatin assembly in response to replication stress.
(A) H2Bub is required for nucleosome assembly near replication forks under replication stress. WT (CFK1204) or htb-K123R (CFK1231) cells were arrested in G1 phase using α-factor, and were then released into 200 mM HU at 30°C for 60 minutes. At the indicated time, cells were collected and histone occupancy at two early origins (ARS305 and ARS607) and one late origin (ARS501) was determined by ChIP using antibodies against H3. IP signals at ARS sequences were normalized to IP signals at TELVI-R. The results are the mean +/− SEM of three replicates. (B) Genetic interactions between H2Bub and histone chaperones (Cac1, Asf1, and Hir1) or a histone acetyl-transferase (Rtt109). Ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains (WT (CFK1204), htb-K123R (CFK1231), cac1Δ (CFK1206), cac1Δ htb-K123R (CFK1237), asf1Δ (CFK1208), asf1Δ htb-K123R (CFK1233), rtt109Δ (CFK1212), rtt109Δ htb-K123R (CFK1241), hir1Δ (CFK1202), and hir1Δ htb-K123R (CFK1235)) were spotted onto YPD plates containing HU (0 or 50 mM), and cell growth was monitored for 2–3 days. (C) The survival of asf1Δ (CFK1208) and asf1Δ htb-K123R (CFK1233) cells in response to acute treatment with HU, as described in Fig. 1A. (D) H2Bub modulates the interaction between Asf1 and Rad53 under HU stress. Asynchronous cultures of WT (YMW105) or htb-K123R (YMW104) cells were untreated (−) or treated (+) with 0.2M HU for 90 minutes. Protein extracts were prepared and incubated with pre-bound anti-HA-protein G beads to pull down Asf1-3×HA, and the immune-precipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, before being probed with either anti-HA or anti-Rad53 antibodies. (E) A working model depicting the role of H2Bub in nucleosome assembly under HU stress. H2Bub coordinates nucleosome assembly in response to replication stress by directly contributing to nucleosome formation and by indirectly regulating the availability of Asf1 during HU stress.