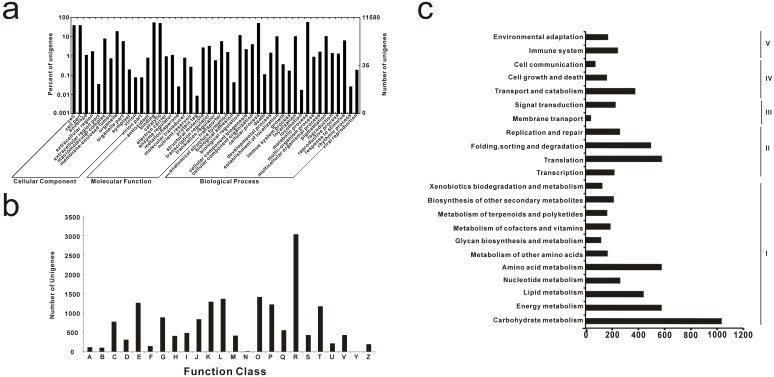
Figure 2. Annotation of common bean unigenes.
a), GO annotation of common bean unigenes. The results are summarized in three main categories: biological process, cellular component, and molecular function. In total, 11,580 genes have been assigned 50 GO terms. In some cases, one gene has multiple terms. b), COG functional annotations of common bean unigenes. A, RNA processing and modification; B, Chromatin structure and dynamics; C, Energy production and conversion; D, Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; E, Amino acid transport and metabolism; F, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; G, Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; H, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, Lipid transport and metabolism; J, Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K, Transcription; L, Replication, recombination and repair; M, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N, Cell motility; O, Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; P, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; R, General function prediction only; S, Function unknown; T, Signal transduction mechanisms; U, Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; V, Defense mechanisms; Y, Nuclear structure; Z, Cytoskeleton. c), Histogram presentation of KEGG classification of unigenes. The all unigenes were assigned X pathways within X clades under five major categories: I, Metabolism; II, Genetic information processing; III, Environmental information processing; IV, Cellular processes; V, Organismal systems.