FIGURE 1.
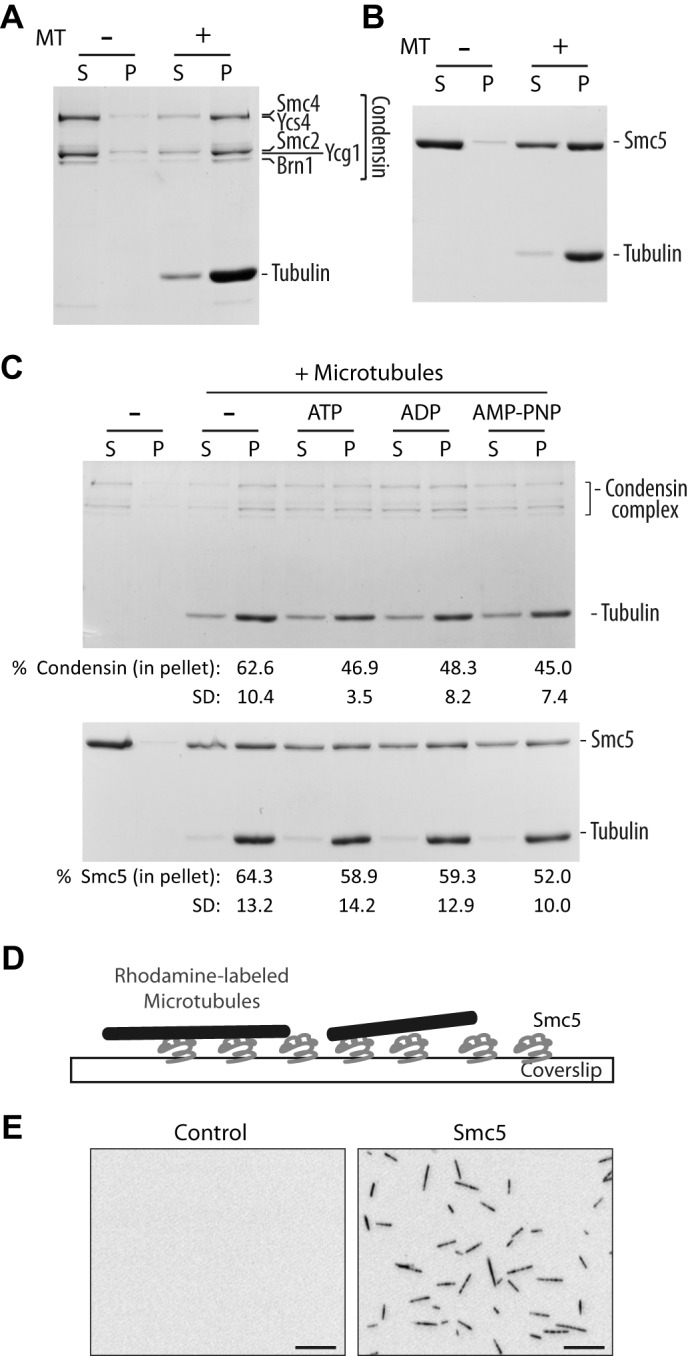
SMC proteins bind directly to microtubules in vitro. A and B, microtubule co-sedimentation assay with condensin complex (A) and monomeric Smc5 (B). Coomassie Blue-stained gels of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions are shown. Microtubules were used at 0.5 μm (calculated for tubulin dimer concentration). Note that due to the large differences in the molecular mass of tubulin and condensin subunits, it is difficult to resolve all individual components of this complex in a single gel while simultaneously visualizing tubulin subunits (hence the appearance of only three major bands at the position of the condensin complex in the gel (18)). The weak band above the major Ycg1-Smc2 band corresponds to phosphorylated Ycg1, as reported previously (18). C, microtubule co-sedimentation assay with condensin complex (top) and Smc5 (bottom) in the presence of buffer alone (−), ATP, ADP, and a non-hydrolyzable analog, AMP-PNP. Microtubules were used at 0.25 and 0.5 μm for condensin complex and Smc5, respectively. The percentage of SMC proteins in the pellet under each condition is shown below the corresponding lane below the Coomassie Blue-stained gel. Averages of four independent experiments are shown, with S.D. D, an illustration depicting the microscopy-based microtubule binding assay. E, representative images of X-Rhodamine-labeled microtubules captured in control (uncoated) or Smc5-coated coverslip. Scale bars, 10 μm.
