FIGURE 4.
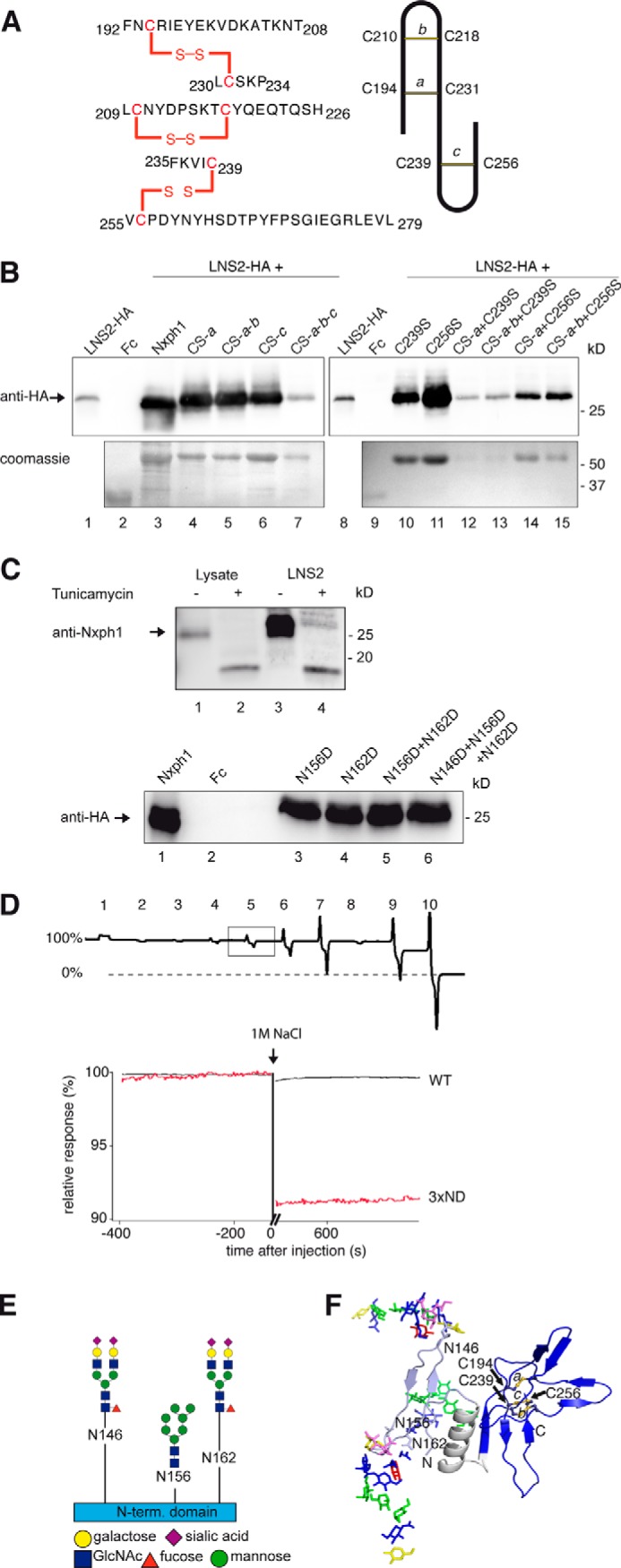
Structural determinants of Nxph1·α-Nrxn complex formation. A, nanoESI quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry of recombinant Nxph1 protein (left panel) reveals a abbacc cysteine connectivity with three bridges (scheme, right panel). B, successive Cys-to-Ser mutations (lanes 4–7), analysis of single mutations (lanes 10–11), and their combinations (lanes 12–15) identify Cys-239 as most sensitive for Nxph1 binding to LNS2 (lanes 12 and 13). C239S reduces secretion of Nxph1 when combined with cysteine bridge a (lanes 12–13); similar combinations with C256S have no effect (lanes 14–15). C, N-glycosylation of Nxph1 is not required for complex formation with LNS2. Binding of recombinant mature Nxph1 to Fc-tagged LNS2 co-expressed in COS7 cells without (lane 3) and with (lane 4) the addition of tunicamycin (upper panel). Successive Asn-to-Asp mutations of all N-glycosylation sites (Asn-146, Asn-156, and Asn-162) did not prevent complex formation (lanes 3–6, lower panel). D, N-glycosylation stabilizes the Nxph1·LNS2 complex. In a reversed surface plasmon resonance experiment, purified Nxph1-Fc·LNS2-HA complex covalently linked to CMD chip was tested to dissolve by serial injection of 100 mm NaOAc pH4 (1), 50 mm Tris, pH 8.9 (2), 250 mm NaCl (3), 500 mm NaCl (4), 1 m NaCl (5), 2 m NaCl (6), 4 m NaCl (7), 5 mm EDTA (8), 6 m urea (9), and 7 m guanidinium chloride (10). The wild-type (WT) complex was not affected by most conditions (the base line not changed, 100% binding) but can be disassembled by denaturing agents (9 and 10), serving as the reference for releasable protein (0% binding). In contrast to WT (square, upper panel; black trace, lower panel), deglycosylation by the triple Asn to Asp mutation (3× ND) released 9% of the complex (red trace, lower panel) after injection of 1 m NaCl. E, glycosylation pattern of the Nxph1 N-terminal domain as determined by mass spectrometry (for details, see Table 1). Residues Asn-146 and Asn-162 were bound to complex type glycans containing fucose and sialic acids, and Asn-156 was linked to high mannose glycans. F, molecular model structure of Nxph1 with glycans attached.
