Figure 5.
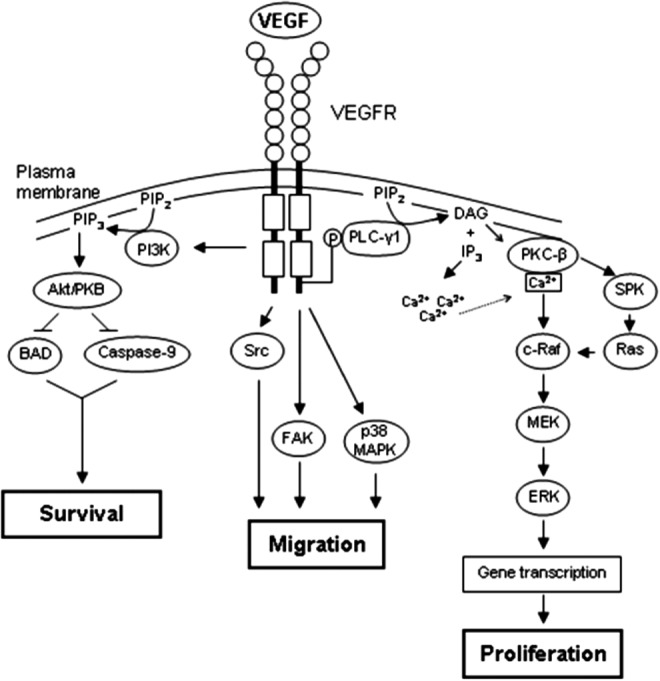
VEGFR signaling. VEGF–VEGFR binding causes dimerization and autophosphorylation of the VEGFR. VEGFR phosphorylation triggers PI3K activation and phosphorylation of Akt. Active Akt blocks the proapoptotic molecules BAD and caspase-9, resulting in cell survival (left). VEGFR signaling also activates several kinases that mediate cell migration, including Src, FAK, and p38 MAPK (middle). Activation of multiple pathways following VEGFR phosphorylation leads to MAPK signaling (phosphorylation of MEK/ERK), which stimulates cellular proliferation (right). Akt/PKB, protein kinase B; BAD, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; SPK, sphingosine kinase.
