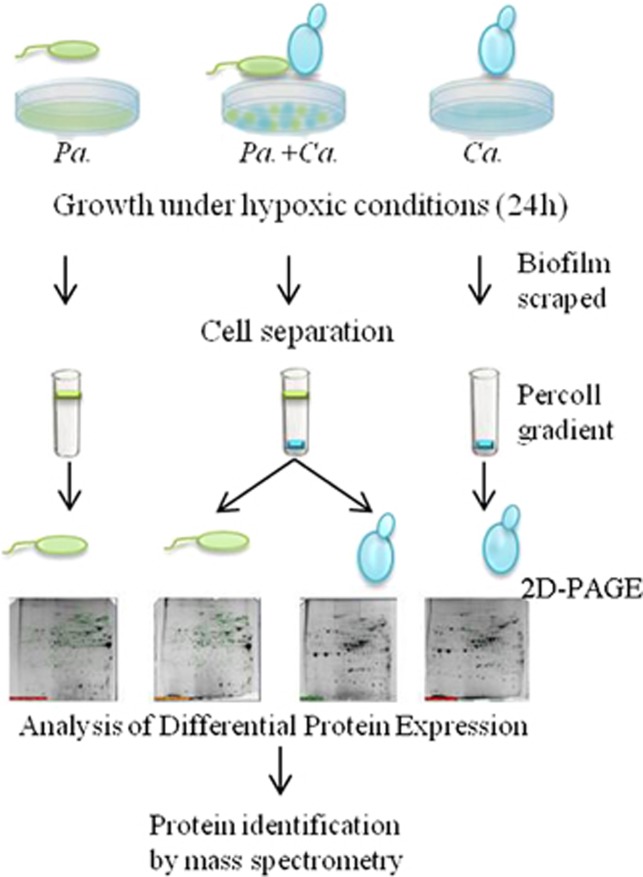
Figure 1.
Experimental design for the proteomic analysis of C. albicans-P. aeruginosa interaction. Single- and mixed-species biofilms were cultured under hypoxic conditions in polystyrene Petri plates. To generate mixed biofilms, we inoculated with P. aeruginosa (Pa.) ∼1.5 × 108 cells ml−1 and ∼1 × 106 C. albicans (Ca.) cells ml−1 in Petri plates at the beginning of each experiment. For the single-species biofilms, the medium initially contained ∼1.5 × 108 bacterial cells ml−1 or ∼1 × 106 yeast cells ml−1. At 24 h postculture, the medium with planktonic cells was removed, and the biofilm at the bottom of the plate was scraped. The fungi and bacteria were separated from the mixed biofilms by centrifugation in a discontinuous Percoll gradient. The monospecific biofilms received the same treatment as the mixed biofilms. Whole-cell proteins of three independent cultures (biological replicates) were analyzed by 2D-PAGE. Spots whose relative expression changed in P. aeruginosa or C. albicans in single versus mixed biofilms were identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.