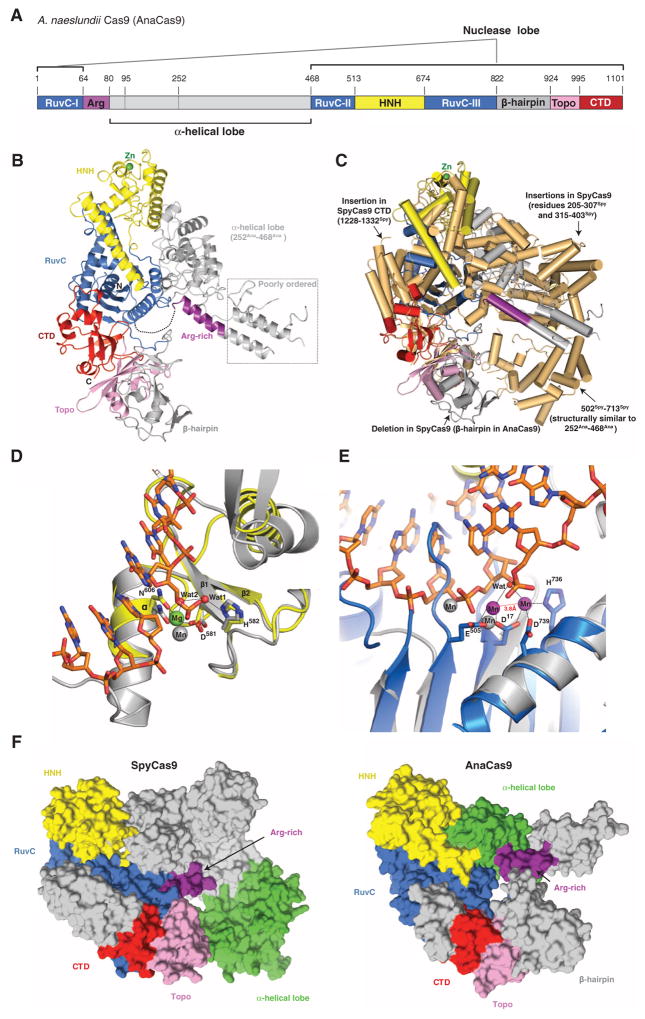
Fig. 3. Crystal structure of AnaCas9 defines the conserved structural core of Cas9 enzymes.
(A) Cartoon schematic of the polypeptide sequence and domain organization for the type II-C Cas9 protein from A. naeslundii (AnaCas9). (B) Overall structure of AnaCas9 shown in ribbon representation. Individual Cas9 domains are colored according to the scheme in (A). A disordered segment connecting a RuvC motif and Arg-rich region is denoted with a dashed line. The disordered region in the helical lobe is denoted with a dotted line box. A green sphere denotes a bound zinc ion in the HNH domain. (C) Superposition of AnaCas9 [colored as in (A)] with SpyCas9 (colored light orange). (D) Close-up view of the active site of AnaCas9 HNH domain (yellow) superimposed with the structure of I-HmuI–DNA complex (PDB entry 1U3E). The DNA cleavage product in the I-HmuI–DNA complex is colored orange, and I-HmuI and its bound Mn2+ ion are colored gray. (E) Close-up view of the AnaCas9 RuvC active site (marine, bound Mn2+ ions shown as purple spheres) overlaid with the structure of RNase H and its bound Mn2+ ions (gray) complexed with a DNA-RNA duplex (orange) (PDB entry 3O3H). (F) Surface representations of SpyCas9 (left panel) and AnaCas9 (right panel) with conserved RuvC, HNH, Arg-rich, Topo-homology, and the conserved cores of the C-terminal domains, colored as in Fig. 1A. The structurally preserved portion of the α-helical lobe is colored green. The nonconserved regions of each protein are colored in gray.