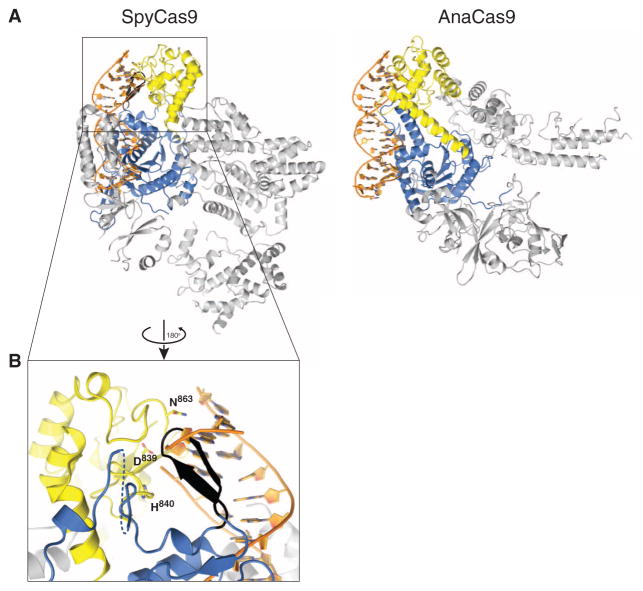
Fig. 4. Both SpyCas9 and AnaCas9 adopt autoinhibited conformations in the apo state.
(A) Models of substrate binding by the HNH domains in SpyCas9 (left) and AnaCas9 (right), based on the superposition of the Cas9 structures with the product-bound complex of the homing endonuclease I-HmuI (PDB entry 1U3E). A 17-bp B-form DNA duplex that covers 3-bp 5′ and 14-bp 3′ of the scissile phosphate is shown. The Cas9 proteins are shown in the same orientation, based on superposition of the respective HNH domains. The HNH domains are depicted in yellow, the RuvC domains are depicted in blue, and residues 1049Spy to 1059Spy of the RuvC domain are shown in black. (B) Zoomed-in view of the HNH domain (yellow) active site in SpyCas9 occluded by the 1049Spy to 1059Spy β-hairpin (black).