Figure 1.
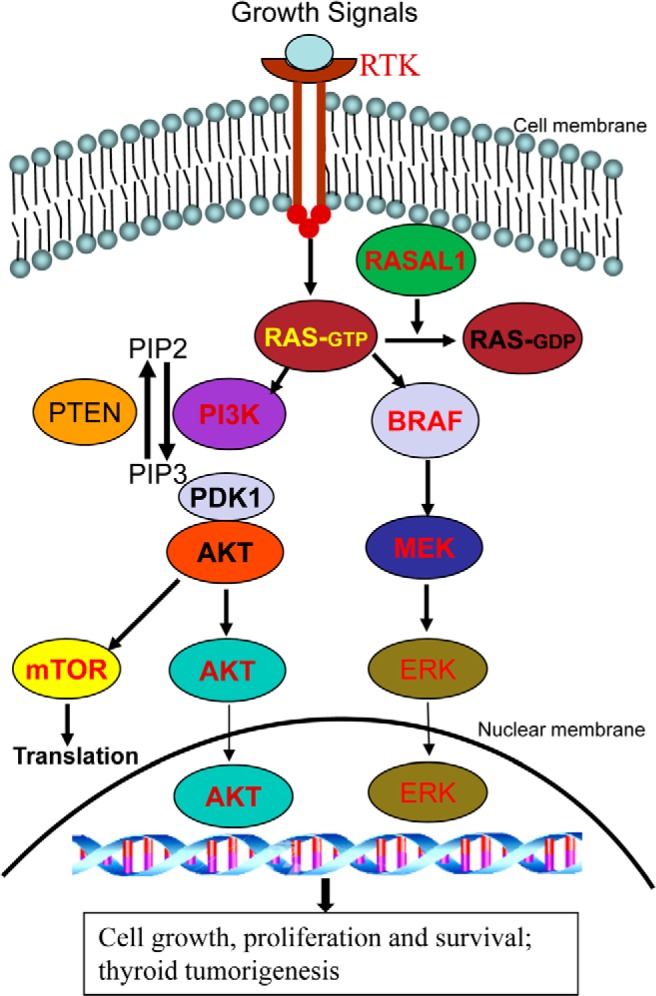
Addition of RASAL1 to the canonical scheme of the RAS-coupled MAPK and PI3K pathways. Shown are the classical RAS-coupled MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways. The normal signaling flow is typically initiated by growth factors acting on various receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) at the cell membrane, which is relayed to RAS, where the downstream MAPK pathway (right side) and PI3K pathway (left side) are activated. Genes for many components in the pathways, such as RTKs, RAS, BRAF, PIK3CA in PI3K, PDK1, AKT, and mTOR are proto-oncogenes, and their activating genetic alterations, such as mutations or copy gains, are the well-established genetic mechanism for the aberrant activation of these pathways in thyroid cancer. PTEN is a tumor suppressor that, by converting phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) to phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2), normally antagonizes the signaling of the PI3K pathway. Genetic or epigenetic inactivation of PTEN results in aberrant activation of the PI3K pathway. RASAL1 as a newly documented prominent tumor suppressor can now be added to this signaling scheme as an important component. As a RAS GTPase-activating protein, RASAL1 normally terminates the RAS signaling by converting the active GTP-bound RAS to the inactive GDP-bound RAS. Genetic or epigenetic inactivation of RASAL1 results in aberrant activation of RAS signaling and the downstream two pathways; this represents a prominent new genetic mechanism for the aberrant activation of the RAS-coupled signaling pathways and thyroid tumorigenesis.
