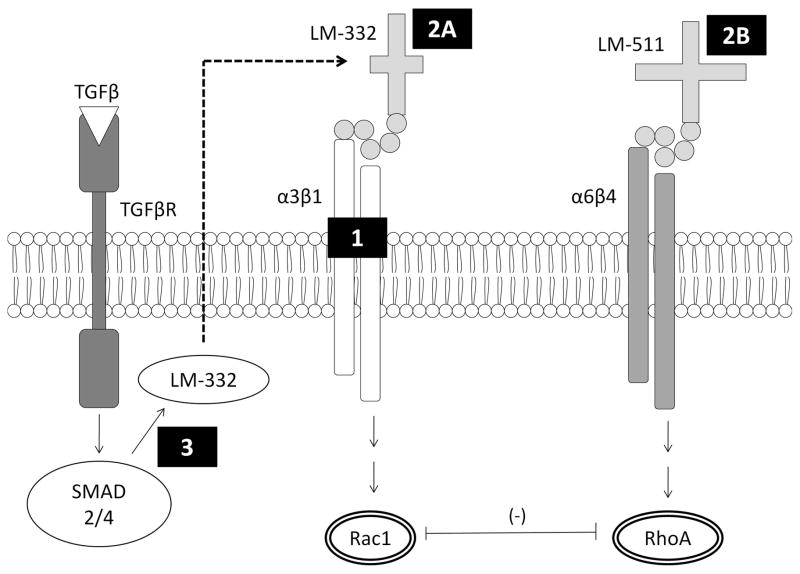
Figure 2. Potential targets for bacterial binding and interference with epithelial restitution.
We hypothesized several points of interaction between P. aeruginosa bacteria and epithelial cells which could lead to inhibition of epithelial restitution. Mechanism 1 involves binding to integrin-α3β1, which is involved in pro-motility signaling through Rac1. Mechanism 2A and 2B involve binding to the extracellular matrix laminins 332 and 511, respectively. Mechanism 3 involves inhibition of LM-332 production by bacteria.